Why Are Native Reserves Important? Understanding Your Local Community

Native reserves, also known as First Nations reserves or Indian reserves, are designated areas of land set aside for Indigenous communities in many countries, including Canada and the United States. These reserves hold immense cultural, historical, and social significance and play a vital role in preserving Indigenous heritage and promoting the well-being of Indigenous peoples. Understanding the importance of native reserves is crucial for fostering meaningful relationships and supporting the rights and aspirations of Indigenous communities.
Preserving Cultural Heritage and Identity

Native reserves serve as bastions of cultural preservation, safeguarding the unique traditions, languages, and customs of Indigenous peoples. Within these reserves, traditional practices and knowledge systems thrive, ensuring the continuity of Indigenous cultures for future generations. The reserves provide a physical space where Indigenous communities can practice their rituals, maintain their cultural artifacts, and pass down their oral histories, thus reinforcing their sense of identity and belonging.
Language Revitalization
Many Indigenous languages are at risk of extinction due to historical oppression and the dominance of colonial languages. Native reserves become vital centers for language revitalization efforts. By providing an environment where Indigenous languages are spoken and taught, these reserves contribute to the preservation and revival of linguistic diversity, which is crucial for maintaining Indigenous cultures and worldviews.
Cultural Centers and Festivals
Native reserves often feature cultural centers, museums, and community spaces that showcase and celebrate Indigenous arts, crafts, music, and history. These centers serve as educational hubs, attracting visitors and fostering cross-cultural understanding. Additionally, many reserves host vibrant festivals and ceremonies, such as powwows and cultural gatherings, which bring together Indigenous communities and visitors, creating opportunities for cultural exchange and celebration.
Sustainable Land Management and Environmental Stewardship

Indigenous peoples have a deep connection to the land and a profound understanding of sustainable land management practices. Native reserves allow Indigenous communities to continue their traditional ways of life, which often include sustainable farming, fishing, hunting, and gathering practices. These practices not only provide for the community’s subsistence but also contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the health of the ecosystem.
Environmental Conservation Efforts
Many native reserves are located in ecologically sensitive areas, and Indigenous communities play a crucial role in protecting these environments. Indigenous knowledge systems, passed down through generations, offer valuable insights into sustainable land use, wildlife conservation, and the management of natural resources. By involving Indigenous communities in environmental decision-making processes, native reserves become important sites for collaborative conservation efforts and the protection of fragile ecosystems.
Promoting Social and Economic Development

Native reserves provide opportunities for Indigenous communities to develop and control their social and economic futures. These reserves often serve as hubs for community-based initiatives, including education, healthcare, and economic development projects. By empowering Indigenous communities to take the lead in decision-making and resource allocation, native reserves contribute to the overall well-being and self-determination of Indigenous peoples.
Community-Led Initiatives
Indigenous communities within native reserves have the autonomy to establish and manage their own institutions and programs. This includes community-run schools, healthcare facilities, and cultural centers. By having control over these essential services, Indigenous communities can tailor them to meet their specific cultural and social needs, ensuring a more holistic and culturally appropriate approach to development.
Economic Opportunities
Native reserves can attract economic development through various means, such as tourism, natural resource management, and the establishment of Indigenous-owned businesses. Tourism, in particular, can provide an economic boost while also offering an opportunity to showcase Indigenous cultures and traditions to a wider audience. Additionally, the sustainable management of natural resources, such as fishing or forestry, can generate income while preserving the environment.
| Reserve | Economic Initiatives |
|---|---|
| Navajo Nation | Tourism, uranium mining, and renewable energy projects |
| Six Nations of the Grand River | Agriculture, tourism, and cultural heritage preservation |
| Haudenosaunee | Traditional crafts, agriculture, and sustainable energy projects |
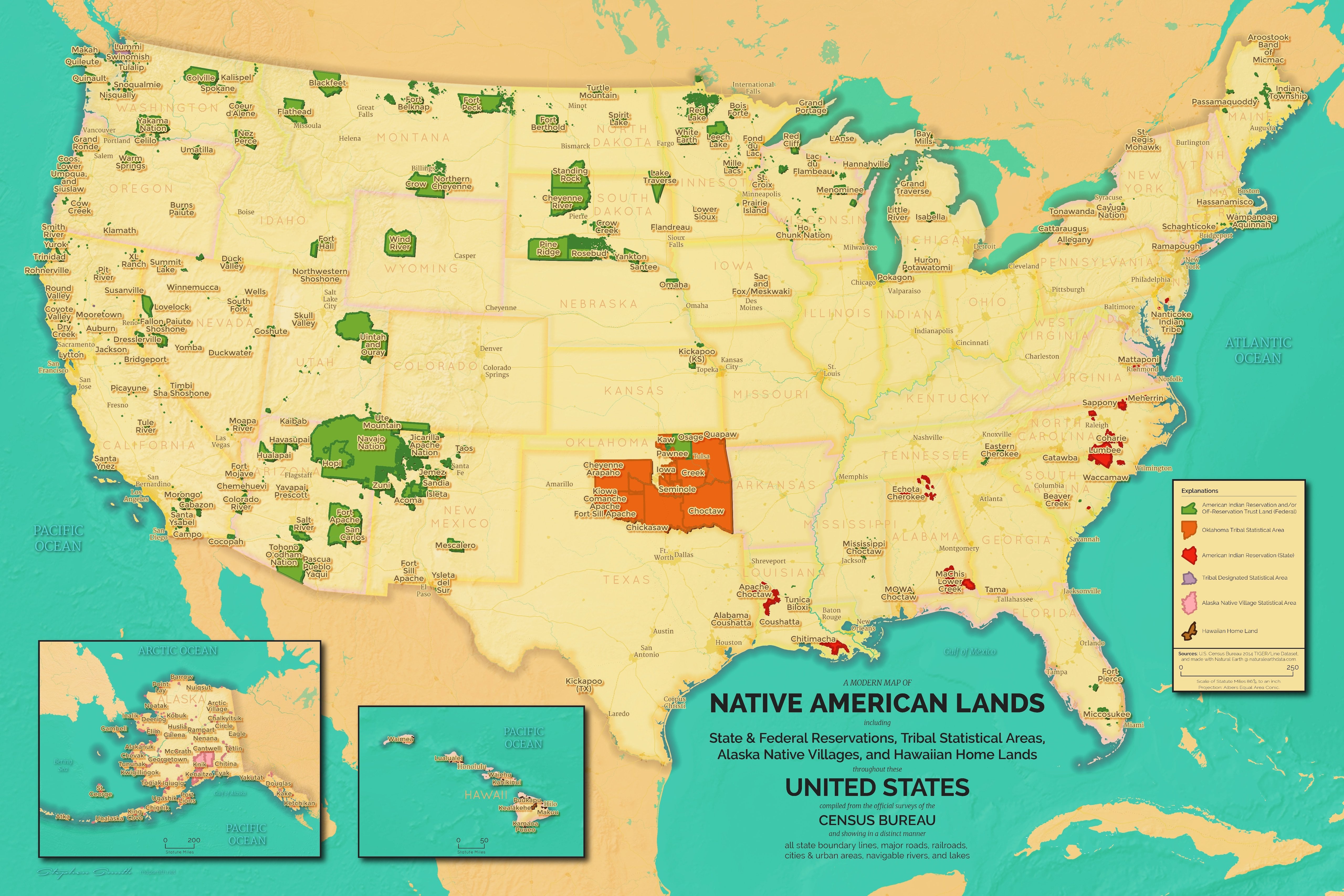
What is the legal status of native reserves, and how are they governed?
+The legal status and governance of native reserves vary depending on the country and the specific Indigenous community. In Canada, for example, reserves are established under the Indian Act, which grants certain rights and responsibilities to Indigenous communities. These rights include land ownership, resource management, and the establishment of community governments. The governance structures within reserves can range from traditional Indigenous systems to more contemporary forms of self-government, depending on the community's preferences and legal frameworks.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How do native reserves contribute to the overall well-being of Indigenous communities?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Native reserves play a crucial role in promoting the well-being of Indigenous communities by providing a sense of cultural identity, self-determination, and economic opportunities. The reserves offer a space where Indigenous peoples can practice their traditions, languages, and customs, which is essential for mental and emotional well-being. Additionally, community-led initiatives and economic development projects within the reserves contribute to improved access to healthcare, education, and social services, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of life for Indigenous residents.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



