Why Are Cucumbers Healthy? A 100G Nutrition Breakdown
Cucumbers, scientifically known as Cucumis sativus, are a popular vegetable with a high water content and a refreshing taste. They are widely cultivated and consumed globally, offering a range of nutritional benefits that contribute to overall health and well-being. This comprehensive analysis will delve into the nutritional composition of cucumbers, highlighting the specific health advantages associated with their consumption.
Nutritional Profile of Cucumbers

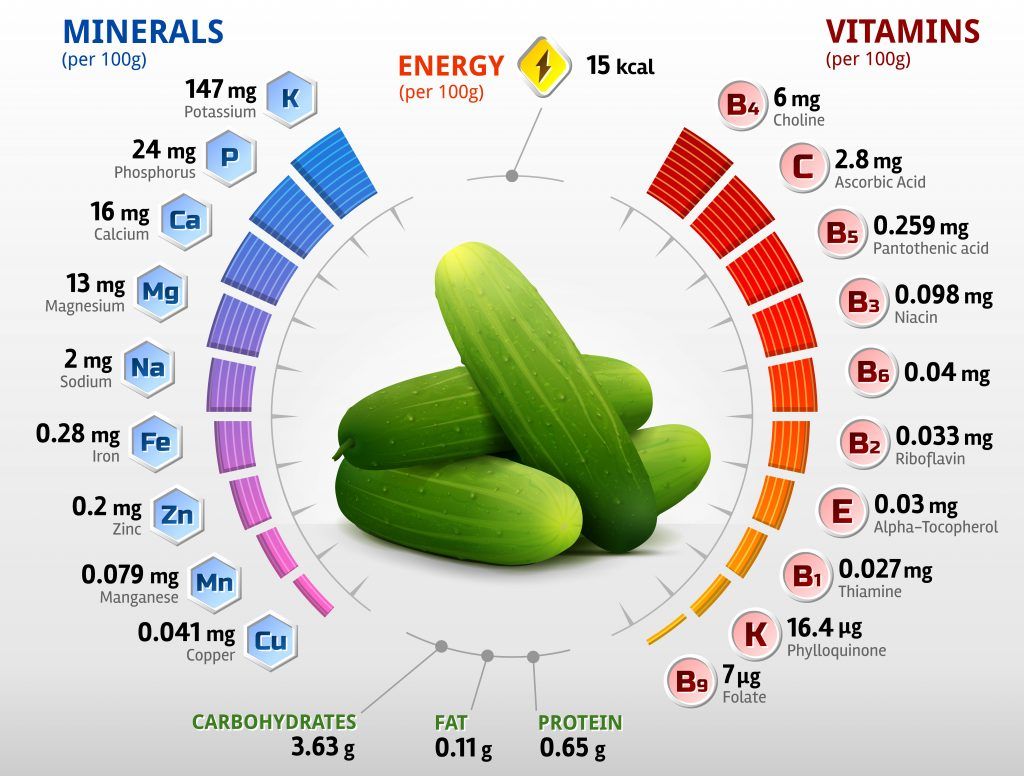
A 100-gram serving of cucumbers, with their skin, provides a diverse array of nutrients, making them a valuable addition to any diet. Here is a detailed breakdown of their nutritional content:
Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health, 100g of cucumbers provide approximately 16.4% of the recommended daily intake.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production. Cucumbers offer around 11.8% of the daily value.
- Potassium: Crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure and proper nerve function. Cucumbers contribute about 2% of the daily requirement.
- Magnesium: Important for muscle and nerve function, as well as bone health. A 100g serving contains roughly 3% of the daily recommended amount.
- Manganese: Acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in various physiological processes. Cucumbers provide approximately 2.8% of the daily value.
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin K | 16.4 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 4.7 mg |
| Potassium | 155 mg |
| Magnesium | 13 mg |
| Manganese | 0.05 mg |

Hydration and Electrolytes
Cucumbers are composed of approximately 95% water, making them an excellent choice for hydration. This high water content also contributes to their low calorie count, with only 16 calories per 100g. Additionally, cucumbers provide essential electrolytes, such as sodium and chloride, which are crucial for maintaining fluid balance and proper muscle function.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
Cucumbers contain a variety of beneficial antioxidants and phytonutrients, including:
- Flavonoids: These compounds have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, contributing to overall health.
- Lignans: Studies suggest that lignans may have a protective effect against certain cancers and heart disease.
- Cucurbitacins: Known for their potential anti-cancer properties, cucurbitacins are unique to cucumbers and other cucurbit vegetables.
Fiber Content
Despite their low calorie content, cucumbers are a good source of dietary fiber. A 100g serving provides around 1.5g of fiber, which aids in digestion, promotes a feeling of fullness, and supports a healthy gut microbiome.
Health Benefits of Cucumber Consumption

Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
The high water content of cucumbers makes them an ideal food for maintaining proper hydration. Adequate hydration is essential for various bodily functions, including digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation. Furthermore, the presence of electrolytes in cucumbers helps to regulate fluid balance and support muscle function.
Digestive Health
The fiber content in cucumbers promotes a healthy digestive system. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, aiding in regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Additionally, the antioxidants and phytonutrients in cucumbers may help reduce inflammation in the gut, supporting overall digestive health.
Cardiovascular Health
The combination of potassium, magnesium, and fiber in cucumbers contributes to a healthy cardiovascular system. Potassium helps to regulate blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium, while magnesium plays a role in maintaining a steady heartbeat. The fiber content also aids in lowering cholesterol levels, further supporting heart health.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
The presence of flavonoids and other antioxidants in cucumbers exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By reducing inflammation, cucumbers may help lower the risk of these diseases.
Skin Health
The high water content and vitamin C in cucumbers contribute to healthy skin. Vitamin C is essential for the production of collagen, a protein that provides structure to the skin. Adequate hydration also plays a crucial role in maintaining skin elasticity and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
Incorporating Cucumbers into Your Diet
Cucumbers are a versatile vegetable that can be enjoyed in various ways. Here are some ideas for incorporating cucumbers into your diet:
- Add sliced cucumbers to salads for a refreshing crunch.
- Make cucumber sandwiches by spreading hummus or avocado on whole-grain bread and topping it with cucumber slices.
- Create a refreshing cucumber soup by blending cucumbers with yogurt, dill, and garlic.
- Include cucumber in your smoothies for added hydration and a subtle flavor.
- Pickle cucumbers for a tangy, crunchy snack.
Can cucumbers help with weight loss?
+Cucumbers can be a valuable addition to a weight loss diet due to their low calorie and high water content. They can help promote a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake. Additionally, the fiber in cucumbers supports a healthy digestive system, which is crucial for weight management.
Are there any potential downsides to consuming cucumbers?
+For most people, cucumbers are safe to consume. However, individuals with certain food allergies or sensitivities may experience allergic reactions. Additionally, cucumbers can contain pesticide residues, so it’s recommended to choose organic varieties or wash them thoroughly before consumption.
How can I get the most nutritional value from cucumbers?
+To maximize the nutritional benefits of cucumbers, it’s best to consume them fresh and raw. Cooking cucumbers can lead to a loss of certain nutrients, especially vitamin C and some phytonutrients. Additionally, eating cucumbers with their skin intact ensures you get the full range of antioxidants and fiber.


