What's The Grasshopper Life Cycle? Uncover The Metamorphosis Journey
The grasshopper, a fascinating insect belonging to the Orthoptera order, undergoes a remarkable life cycle that involves a metamorphosis journey. This process, known as hemimetabolism, is characterized by gradual and incomplete transformation, unlike the complete metamorphosis seen in butterflies and beetles. Understanding the grasshopper's life cycle provides valuable insights into their biology, behavior, and ecological significance. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the various stages of the grasshopper's life, from egg to adult, shedding light on their development, habitat preferences, and the role they play in ecosystems.
The Grasshopper Life Cycle: A Journey of Growth and Adaptation

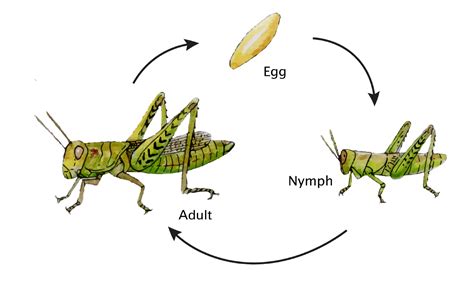
The grasshopper's life cycle is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of these insects. It begins with the egg stage, where female grasshoppers lay their eggs in the soil or on vegetation, often in batches known as egg pods. These eggs, protected by a hard outer casing, undergo a period of development, typically during the warmer months. As the eggs hatch, they give rise to the next stage: nymphs, which are essentially immature grasshoppers.
Nymphs: The Early Stages of Growth
Nymphs are small, wingless versions of adult grasshoppers. They emerge from the eggs with a voracious appetite, feeding on a variety of plant materials. As they grow, they undergo a series of molts, shedding their exoskeletons to accommodate their increasing size. This process, known as ecdysis, occurs multiple times during the nymphal stage, with each molt resulting in a larger, more developed individual. Nymphs are often characterized by their bright colors and active behavior, as they explore their environment and learn crucial survival skills.
One of the most fascinating aspects of nymph development is the gradual emergence of wings. As they molt, wing pads become more prominent, eventually developing into fully functional wings. This process, coupled with the growth of other vital organs, prepares the nymphs for their transition into adulthood.
| Nymphal Stage | Developmental Milestones |
|---|---|
| First Instar | Initial emergence, feeding, and exploration |
| Second to Fifth Instar | Multiple molts, wing pad development, and increased size |
| Pre-Adult Stage | Final molt, emergence of functional wings, and preparation for adulthood |

Adult Grasshoppers: The Reproductive Stage
Upon reaching the pre-adult stage, grasshoppers undergo their final molt, transforming into adults. This stage marks the completion of their metamorphosis journey. Adult grasshoppers are characterized by their fully developed wings, which enable them to fly and disperse over larger areas. They also possess reproductive organs, allowing them to engage in mating and egg-laying activities.
The reproductive behavior of grasshoppers is intriguing. Males often produce distinctive sounds, known as stridulation, to attract females. This process involves rubbing specialized structures on their wings or legs together, creating a unique acoustic signal. Once a pair mates, the female grasshopper seeks an appropriate site to lay her eggs, thus completing the life cycle.
Environmental Factors and Habitat Preferences
The grasshopper's life cycle is intimately linked to its environment. Different species of grasshoppers exhibit preferences for specific habitats, such as grasslands, meadows, or agricultural fields. The availability of suitable food sources, shelter, and breeding sites plays a crucial role in their survival and reproduction.
Environmental factors, such as temperature and moisture levels, also influence the timing and duration of the grasshopper's life cycle. Warmer temperatures generally accelerate development, while cooler conditions can slow down the process. Additionally, the availability of resources, including food and water, can impact the survival and health of grasshoppers at various stages of their life cycle.
Ecological Significance and Impact
Grasshoppers play a significant role in ecosystems as both consumers and food sources. As herbivores, they feed on a variety of plant materials, including leaves, stems, and seeds. This feeding behavior can have both positive and negative impacts. While grasshoppers contribute to nutrient cycling and the dispersal of plant seeds, excessive feeding can lead to crop damage and ecological imbalances.
Furthermore, grasshoppers serve as a vital food source for many predators, including birds, reptiles, and insects. Their high nutritional value makes them an important component of the food web, contributing to the overall health and diversity of ecosystems. Understanding the grasshopper's life cycle is essential for managing their populations and mitigating their impact on agriculture and natural habitats.
Conclusion: A Complex and Dynamic Life Cycle

The grasshopper's life cycle is a complex and dynamic process, characterized by gradual transformation and adaptation. From the egg stage to adulthood, grasshoppers undergo a series of changes, each with its own unique challenges and milestones. Understanding this life cycle provides valuable insights into their biology, behavior, and ecological role.
By studying the grasshopper's life cycle, scientists and ecologists can develop effective strategies for pest management, conservation, and the sustainable use of natural resources. Furthermore, the grasshopper's ability to adapt and thrive in various environments serves as a reminder of the resilience and diversity of life on our planet.
How long does the grasshopper's life cycle typically last?
+The duration of the grasshopper's life cycle can vary depending on species and environmental conditions. On average, it takes several weeks to several months for grasshoppers to complete their life cycle, from egg to adult. Factors such as temperature, moisture, and food availability can influence the timing and pace of their development.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some common predators of grasshoppers?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Grasshoppers have a diverse range of predators, including birds, reptiles, mammals, and other insects. Birds, such as songbirds and raptors, are known to feed on grasshoppers, especially during their nymphal stages. Reptiles like lizards and snakes also prey on grasshoppers, while mammals like bats and rodents may consume them as well. Additionally, other insects, such as parasitic wasps and flies, can parasitize grasshopper eggs and nymphs.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How do grasshoppers contribute to nutrient cycling in ecosystems?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Grasshoppers play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by feeding on plant materials and converting them into nutrient-rich waste. As they feed, grasshoppers break down complex plant compounds, releasing nutrients back into the soil. This process enhances soil fertility and supports the growth of other plants, contributing to the overall health and productivity of ecosystems.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>