What Makes Eastern Cedar Trees So Special? A Comprehensive Guide
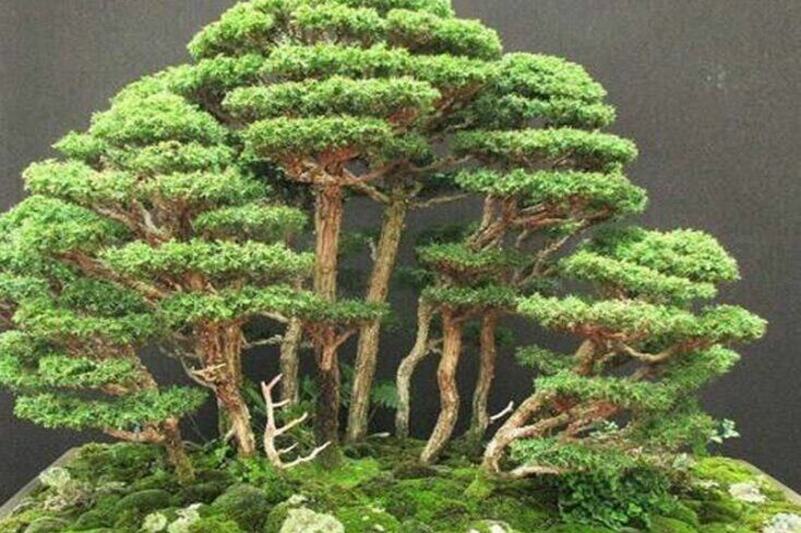

Eastern cedar trees, scientifically known as Thuja occidentalis, are an iconic species native to North America, particularly thriving in the eastern regions. These evergreen conifers possess a rich history and a multitude of unique characteristics that have made them a beloved and valuable component of various ecosystems and industries. From their cultural significance to their ecological importance and practical applications, Eastern cedars have left an indelible mark on both natural and human environments.
Historical and Cultural Significance

The Eastern cedar tree has a long and profound connection with human history and culture. Indigenous peoples across North America have utilized these trees for centuries, valuing them for their medicinal properties, building materials, and spiritual significance.
Medicinal Uses
The therapeutic benefits of Eastern cedar have been recognized for generations. Indigenous communities have employed various parts of the tree, such as the bark, leaves, and oil, to treat a range of ailments. The inner bark, for instance, was often used to create a tea with potential anti-inflammatory properties, while the essential oil extracted from the leaves and twigs has been utilized in traditional medicine for its antiseptic and analgesic qualities.
Cultural and Spiritual Significance
Eastern cedars hold a sacred place in the beliefs and practices of many Indigenous cultures. They are often associated with protection, purification, and spiritual connection. The aromatic cedar wood is used in smudging ceremonies, where the smoke is believed to cleanse and purify the surroundings, both physically and spiritually. Additionally, the tree’s resilience and longevity have made it a symbol of strength and endurance in many cultural narratives.
Ecological Importance
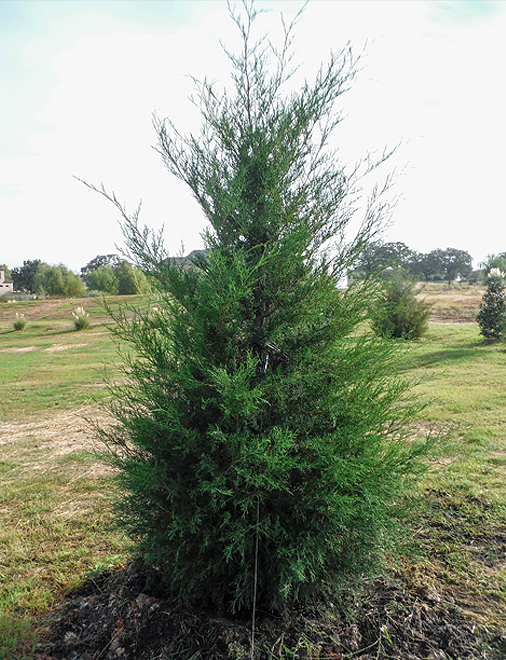

Beyond their cultural significance, Eastern cedar trees play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of their native habitats. These trees are a cornerstone species, providing a multitude of benefits to the ecosystems they inhabit.
Habitat and Biodiversity
Eastern cedars are known for their ability to create unique and diverse habitats. They provide essential shelter and food for a wide array of wildlife, including birds, small mammals, and insects. The dense foliage of these trees offers protection from predators and the elements, while the seeds and berries produced by Eastern cedars serve as a crucial food source during the winter months.
Additionally, the complex root systems of Eastern cedars help prevent soil erosion, especially in areas with sloping terrain. By stabilizing the soil, these trees contribute to the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem, ensuring that other plant and animal species can thrive.
Carbon Sequestration
Like all trees, Eastern cedars play a critical role in mitigating climate change through carbon sequestration. Through the process of photosynthesis, these trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their tissues, helping to reduce the concentration of this greenhouse gas. This natural carbon capture and storage mechanism is a vital component of efforts to combat global warming.
Physical Characteristics and Adaptations

Eastern cedar trees are renowned for their distinctive features and remarkable adaptations that enable them to thrive in a variety of environments.
Growth and Size
These trees exhibit a slow to moderate growth rate, reaching heights of up to 40-50 feet (12-15 meters) with a spread of 15-25 feet (4.5-7.6 meters) when mature. Their pyramidal or columnar shape, characterized by a central leader and horizontal branching, makes them an aesthetically pleasing choice for landscaping and ornamental purposes.
Adaptations to Cold and Snow
Eastern cedars are well-adapted to the cold and snowy conditions of their native range. Their dense, scaly foliage helps protect the tree from harsh winter winds and heavy snowfall. Additionally, the tree’s ability to retain its needles year-round, a characteristic known as evergreen persistence, ensures a continuous photosynthetic process even during the colder months.
Resistance to Pests and Diseases
Eastern cedars are known for their resistance to many common pests and diseases that affect other tree species. This resilience is partly attributed to their thick, fibrous bark, which acts as a protective barrier against potential threats. However, like all plants, Eastern cedars are not entirely immune to pests and diseases, and certain conditions can make them susceptible to issues such as bagworm infestations or cedar-apple rust.
Practical Applications and Uses

The versatility of Eastern cedar trees extends beyond their ecological and cultural significance, as they have a wide range of practical applications in various industries.
Construction and Woodworking
Eastern cedar wood is highly valued in the construction and woodworking industries due to its durability, resistance to decay, and distinctive aroma. The wood’s natural oils act as a built-in preservative, making it an excellent choice for outdoor projects such as fencing, decking, and siding. Additionally, its straight grain and fine texture make it a preferred material for intricate woodworking projects and furniture making.
Landscaping and Ornamental Uses
The aesthetic appeal of Eastern cedar trees, coupled with their adaptability to a range of soil and climate conditions, makes them a popular choice for landscaping and ornamental purposes. They are often used as windbreaks, privacy screens, or as a focal point in gardens and parks. The tree’s ability to tolerate urban conditions, such as air pollution and limited space, further enhances its value in urban landscaping projects.
Essential Oils and Aromatherapy
The essential oil extracted from Eastern cedar trees has found its way into the world of aromatherapy and natural medicine. Known for its fresh, woody scent, cedar oil is often used in aromatherapy to promote relaxation, improve concentration, and alleviate stress. Additionally, its antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties make it a popular ingredient in natural skincare and cosmetic products.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Height | Up to 40-50 feet (12-15 meters) |
| Spread | 15-25 feet (4.5-7.6 meters) |
| Growth Rate | Slow to moderate |
| Shape | Pyramidal or columnar |
| Leaf Type | Scaly, evergreen |
| Bark | Thick, fibrous |
| Wood Properties | Durable, decay-resistant, aromatic |

What are some common cultivars of Eastern cedar trees, and what are their unique characteristics?
+There are several popular cultivars of Eastern cedar trees, each with its own distinct features. Some notable examples include the Thuja occidentalis ‘Smaragd’, which is known for its dense, bright green foliage and compact growth habit, making it an excellent choice for hedges and topiary. The ‘Nigra’ cultivar, on the other hand, features dark green foliage that turns a deep bronze-green in the winter, adding a unique color contrast to the landscape.
Are Eastern cedar trees suitable for all types of soil and climate conditions?
+Eastern cedar trees are highly adaptable and can tolerate a wide range of soil and climate conditions. They thrive in well-drained soils, but can also grow in clay or loamy soils. While they prefer full sun, they can tolerate partial shade as well. However, it’s important to note that extreme heat and drought conditions can stress the tree, so providing adequate water during dry periods is crucial.
How do Eastern cedar trees contribute to the local economy and industries?
+Eastern cedar trees have a significant economic impact on local communities and industries. The wood and essential oils derived from these trees are valuable commodities, supporting various sectors such as construction, woodworking, and aromatherapy. Additionally, the tourism industry benefits from the aesthetic appeal of Eastern cedar landscapes, attracting visitors and boosting local economies.