Us Army Cav Scout

The United States Army Cavalry Scout is a highly specialized and critical role within the military, serving as the eyes and ears of the battlefield. These scouts are trained to gather intelligence, conduct reconnaissance missions, and provide vital information to support military operations. With a rich history dating back to the early 20th century, the Cavalry Scout has evolved into a modern-day warrior, utilizing advanced technology and tactics to ensure mission success.
The Role and Responsibilities of an Army Cavalry Scout

Cavalry Scouts, often referred to as “Cav Scouts,” are integral to the success of any military operation. Their primary role is to gather and analyze intelligence, which involves conducting surveillance, monitoring enemy movements, and collecting data on terrain, weather, and potential targets. This information is crucial for commanders to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
Additionally, Cav Scouts are trained in a variety of specialized skills, including advanced driving and navigation techniques, radio and communication operations, and the use of advanced surveillance equipment. They are often deployed in small teams, working in close coordination with other military units to gather intelligence and provide real-time updates.
Key Responsibilities and Skills
- Conducting reconnaissance missions: Cavalry Scouts plan and execute missions to gather intelligence, often operating behind enemy lines or in hostile territories.
- Surveillance and target acquisition: They employ various surveillance techniques, including aerial and ground-based methods, to identify and track enemy targets.
- Map reading and navigation: Proficiency in reading maps and using navigation tools is essential for Cav Scouts to navigate through unfamiliar territories.
- Communication and radio operations: Effective communication is vital. Scouts are trained to use radios and other communication equipment to transmit intelligence data accurately.
- Vehicle operations: Many missions involve the use of vehicles, so scouts must be skilled in driving and maintaining a variety of military vehicles.
- Physical fitness and endurance: The nature of their work demands high levels of physical fitness and endurance, as scouts often operate in challenging and dangerous environments.
Training and Qualifications

Becoming an Army Cavalry Scout is a rigorous process that requires a combination of physical, mental, and technical skills. Prospective scouts must undergo a series of assessments and training programs to ensure they possess the necessary attributes.
Basic Requirements
- Meet the minimum age requirement (usually 18 years old)
- Be a U.S. citizen or permanent resident
- Pass a thorough background check
- Achieve a minimum score on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Be in excellent physical condition and pass a rigorous fitness assessment
Training Process
- Basic Combat Training (BCT): This initial phase focuses on building physical fitness, discipline, and basic military skills. Scouts learn about weapons handling, field craft, and military customs.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): In this phase, scouts receive specialized training in cavalry operations. They learn about reconnaissance techniques, surveillance methods, and the use of advanced technology.
- Unit-level Training: After completing AIT, scouts join their assigned units and continue their training. This phase involves practical exercises, field training, and mission-specific preparation.
- Ongoing Professional Development: Cavalry Scouts must continuously update their skills and knowledge. They attend regular training sessions, participate in exercises, and undergo periodic evaluations to maintain their proficiency.
Equipment and Technology
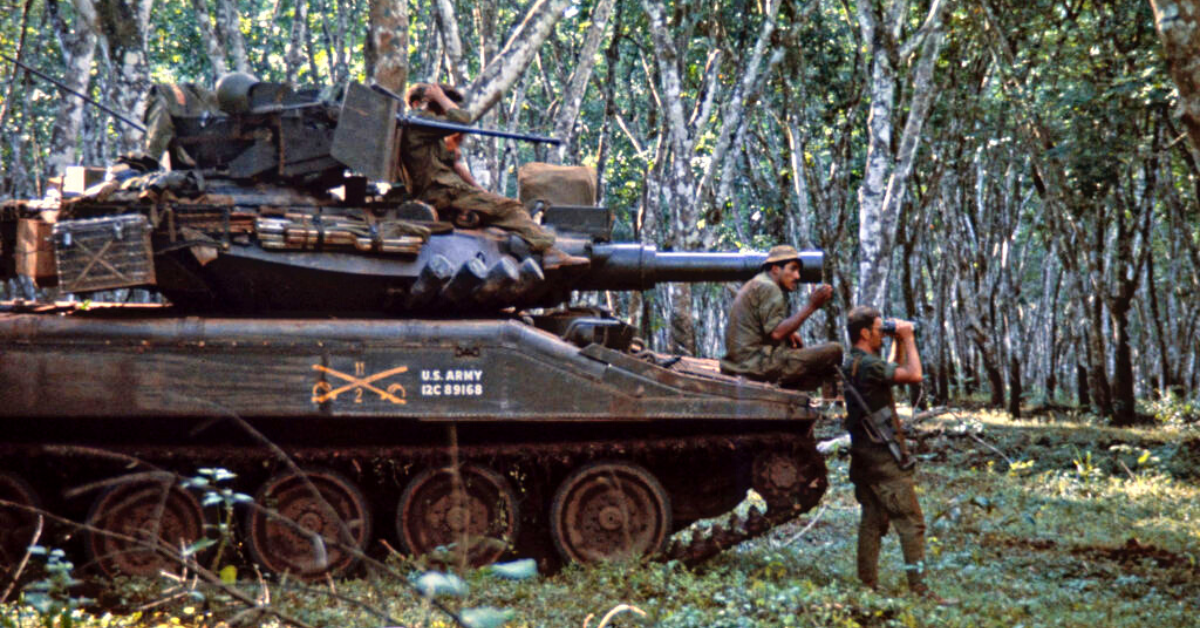

Army Cavalry Scouts utilize a range of advanced equipment and technology to carry out their missions effectively. From state-of-the-art surveillance systems to specialized vehicles, their toolkit is designed to provide them with a tactical advantage on the battlefield.
Surveillance and Reconnaissance Gear
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: These devices allow scouts to detect heat signatures, providing a significant advantage in low-light or nighttime operations.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Small drones equipped with cameras and sensors are used for aerial reconnaissance, enabling scouts to gather intelligence from a safe distance.
- Night Vision Goggles: Essential for nighttime operations, these goggles enhance the scout’s vision in low-light conditions, ensuring they can navigate and gather intelligence effectively.
- Advanced Binoculars: High-quality binoculars with built-in range finders and image stabilization are used for long-range surveillance and target acquisition.
Vehicles and Mobility
Cavalry Scouts often operate from a variety of military vehicles, including:
- Humvees: These versatile vehicles provide mobility and can be equipped with various weapons and surveillance systems.
- Light Reconnaissance Vehicles (LRVs): Designed for rapid deployment and maneuverability, LRVs are often used for reconnaissance missions.
- Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs): Robotic platforms used for reconnaissance and explosive ordnance disposal, reducing the risk to scouts.
Historical Perspective

The concept of cavalry scouts has its roots in the early 20th century, when the U.S. Army recognized the need for specialized reconnaissance units. During World War I, cavalry scouts played a crucial role in gathering intelligence and providing vital information to commanders. With the advancement of technology, the role of cavalry scouts has evolved, but their importance in modern warfare remains undisputed.
Evolution of Cavalry Scouts
- World War I: Cavalry scouts primarily relied on horses for mobility, conducting reconnaissance missions on the Western Front. Their role was crucial in providing real-time intelligence to commanders.
- World War II: With the introduction of mechanized warfare, cavalry scouts transitioned to using motorcycles and jeeps for mobility. They played a vital role in the North African and European theaters, gathering intelligence and supporting ground troops.
- Modern Era: In recent decades, the role of cavalry scouts has expanded to include a wider range of technologies and tactics. They now utilize advanced surveillance equipment, unmanned vehicles, and specialized training to meet the challenges of modern warfare.
Challenges and Future Prospects

While the role of Army Cavalry Scouts is critical, it also presents unique challenges. The nature of their work often puts them in harm’s way, requiring them to operate in high-risk environments. Additionally, the rapid advancement of technology and the changing nature of warfare necessitate continuous adaptation and innovation.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
- Adapting to Emerging Technologies: Cavalry Scouts must stay abreast of the latest advancements in surveillance and reconnaissance technology. This includes learning to operate new equipment and integrating it into their missions effectively.
- Countering Asymmetric Warfare: With the rise of asymmetric warfare, scouts must be prepared to face unconventional threats and adapt their tactics accordingly.
- Enhancing Data Analysis: As scouts gather vast amounts of intelligence data, there is a growing need for advanced data analysis tools and techniques to extract meaningful insights quickly.
- Collaboration and Interoperability: Working closely with other military units and allies is crucial. Scouts must be able to share intelligence data seamlessly and coordinate their efforts effectively.
Conclusion

Army Cavalry Scouts are an essential component of modern military operations, providing crucial intelligence and reconnaissance support. Their specialized training, advanced equipment, and unwavering dedication make them a force to be reckoned with on the battlefield. As the nature of warfare continues to evolve, so too will the role and capabilities of these highly skilled warriors.
What are the physical requirements for becoming an Army Cavalry Scout?
+Prospective Cavalry Scouts must pass a rigorous physical fitness assessment. This typically includes a combination of strength, endurance, and agility tests. Specific requirements may vary, but generally, scouts are expected to excel in activities such as running, swimming, and weightlifting.
How long does it take to become a fully trained Cavalry Scout?
+The training process for Cavalry Scouts is extensive and can take several months. After completing Basic Combat Training (BCT), scouts undergo Advanced Individual Training (AIT) and then join their assigned units for further training. The entire process can range from 6 to 12 months, depending on the individual’s progress and the specific requirements of their unit.
What are some of the most common missions for Cavalry Scouts?
+Cavalry Scouts are involved in a wide range of missions, including:
- Reconnaissance and Surveillance: Scouts gather intelligence on enemy movements, terrain, and potential targets.
- Route Clearance: They conduct patrols and clear routes to ensure the safe movement of military convoys.
- Counter-Insurgency Operations: Scouts often work in urban environments, providing intelligence and support to counter-insurgency efforts.
- Special Operations: Cavalry Scouts may be part of specialized teams conducting high-risk missions behind enemy lines.