Snap Benefits Increase

The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps, is a vital safety net for millions of Americans, providing essential nutritional support to low-income households. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need to enhance SNAP benefits to better address food insecurity and promote healthier dietary choices. This article delves into the recent initiatives and proposals aimed at increasing SNAP benefits, exploring their potential impact and the underlying rationale.
Understanding the Need for Increased SNAP Benefits
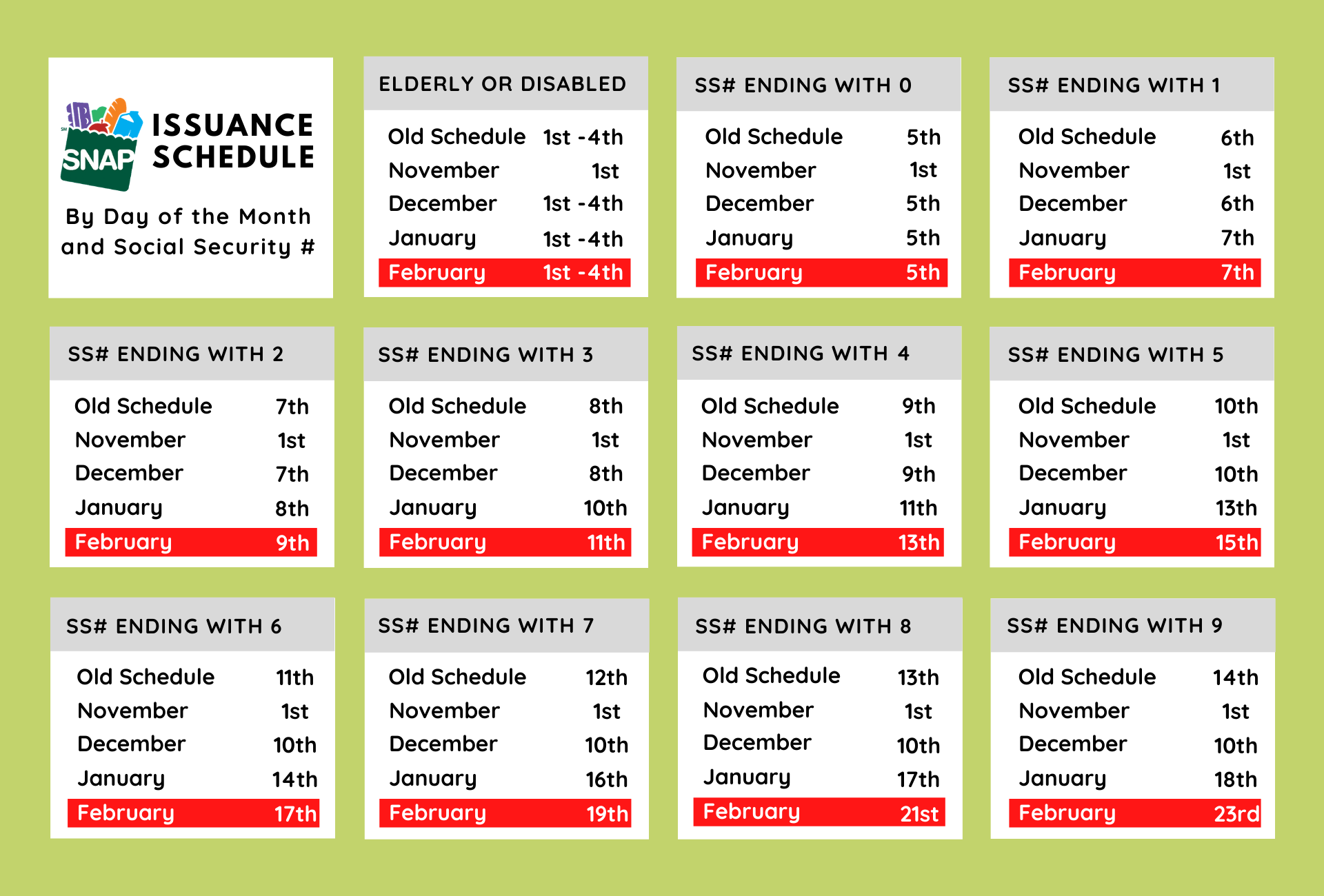
The current SNAP benefit structure is designed to provide a nutritional safety net for individuals and families facing economic challenges. However, several factors have highlighted the need for adjustments to ensure that SNAP effectively fulfills its purpose.
Addressing Food Insecurity
Food insecurity remains a significant issue in the United States, with an estimated 38.3 million people living in households that struggled to access adequate food in 2020. SNAP plays a crucial role in mitigating this issue, but the benefits often fall short of covering the cost of a healthy diet, especially for larger families or those with specific dietary needs.
A study conducted by the Urban Institute in 2018 found that SNAP benefits, on average, cover only 60-80% of the cost of a thrifty food plan, which is the USDA's lowest-cost food plan. This leaves many SNAP recipients unable to afford a nutritionally adequate diet, particularly towards the end of the month when benefits have been exhausted.
Promoting Healthier Eating Habits
The SNAP program not only aims to alleviate hunger but also to encourage healthier eating habits. However, the current benefit structure may inadvertently contribute to poor dietary choices due to the limited purchasing power of SNAP benefits.
A report by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities highlights that the average monthly SNAP benefit per person is approximately $121.00, which often translates to less than $4.00 per day for food. This amount may not be sufficient to purchase fresh produce, whole grains, and other healthy food items, leading to a reliance on cheaper, less nutritious options.
Initiatives and Proposals for SNAP Benefit Increases
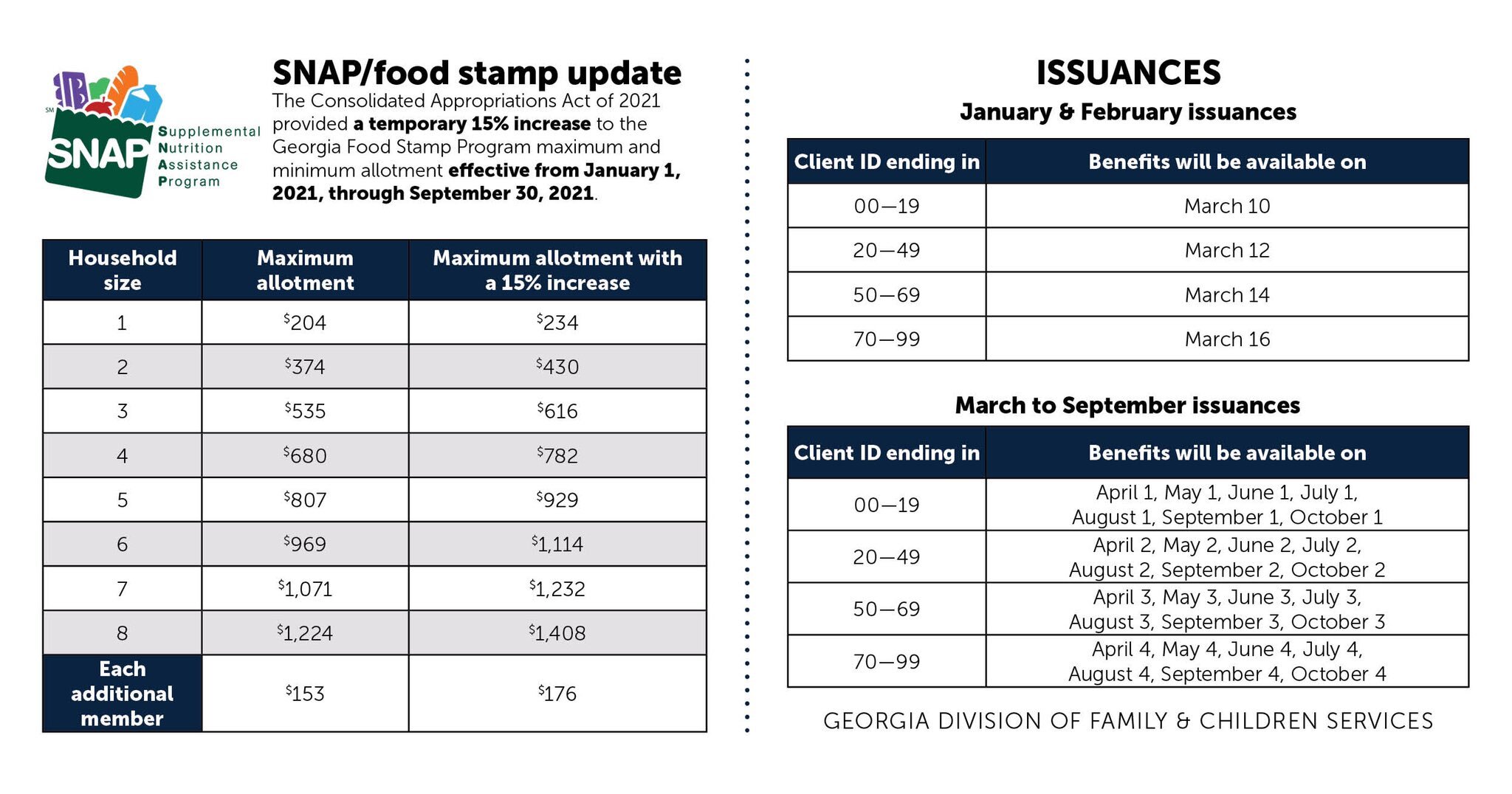
Recognizing the limitations of the existing SNAP benefit structure, various initiatives and proposals have emerged to enhance the program’s effectiveness in combating food insecurity and promoting healthier diets.
The Great Recession and SNAP Expansion
The Great Recession of 2007-2009 saw a significant increase in food insecurity, prompting Congress to temporarily boost SNAP benefits through the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA). This boost, known as the SNAP Emergency Benefit, provided an additional $20.00 per person per month for each SNAP recipient, resulting in a substantial reduction in food insecurity rates.
The success of this temporary measure led to calls for making the increase permanent, but the proposal faced opposition and was ultimately not implemented.
The Pandemic and Emergency SNAP Increases
The COVID-19 pandemic brought renewed attention to the importance of SNAP benefits, as millions of Americans faced job losses and economic hardship. In response, the Families First Coronavirus Response Act (FFCRA) was enacted, which included a 15% increase in SNAP benefits for all recipients, starting in April 2020.
This emergency increase, known as the SNAP Pandemic Electronic Benefits Transfer (P-EBT), provided a vital source of nutritional support during the pandemic, helping to mitigate the impact of economic disruption on food security.
The Farm Bill and Proposed SNAP Reforms
The Farm Bill, a comprehensive piece of legislation that governs agricultural and food policies in the United States, is a key avenue for proposing and implementing SNAP reforms. Over the years, various proposals have been put forth to increase SNAP benefits and improve the program’s effectiveness.
One notable proposal, introduced by Senator Bernie Sanders and Representative Ilhan Omar, aims to double SNAP benefits and eliminate the asset test for eligibility. This proposal, known as the Hunger-Free Communities Act, seeks to ensure that all SNAP recipients have access to sufficient resources for a healthy diet.
Another proposal, put forward by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, suggests increasing SNAP benefits by 20% and enhancing the program's flexibility to better meet the needs of low-income households. This proposal aims to address the current gap between SNAP benefits and the actual cost of a healthy diet.
Impact and Analysis of Increased SNAP Benefits

Increasing SNAP benefits has the potential to significantly impact the lives of low-income Americans, improving food security and dietary quality. Here’s a closer look at the potential effects and considerations surrounding these increases.
Reducing Food Insecurity
The primary goal of increasing SNAP benefits is to reduce food insecurity among low-income households. By providing more generous benefits, SNAP can ensure that individuals and families have access to an adequate and nutritious diet, promoting overall health and well-being.
Research conducted by the USDA's Economic Research Service suggests that a 10% increase in SNAP benefits could lead to a 2-3% reduction in food insecurity rates. This indicates that even modest increases in benefits can have a tangible impact on the lives of SNAP recipients.
Improving Dietary Quality
Enhancing SNAP benefits can also encourage recipients to make healthier food choices. With increased purchasing power, SNAP recipients may be more likely to choose fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and other nutritious foods, leading to improved dietary habits and potentially reducing the risk of diet-related health issues.
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that higher SNAP benefits were associated with increased fruit and vegetable consumption among low-income adults. This suggests that increasing benefits can be an effective strategy for promoting healthier diets among SNAP recipients.
Economic Impact
Increasing SNAP benefits can have a positive economic impact, both on a micro and macro level. For individuals and families, higher SNAP benefits can free up resources for other essential needs, such as housing, healthcare, and education. This can lead to improved financial stability and well-being.
On a larger scale, SNAP is a significant driver of economic activity. A report by the Moody's Analytics estimates that every $1.00 increase in SNAP benefits generates $1.50 in economic activity. This multiplier effect can stimulate local economies, particularly in areas with high rates of food insecurity and unemployment.
Challenges and Considerations
While increasing SNAP benefits has numerous potential benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
One concern is the potential for increased program costs. SNAP is already one of the largest federal programs, and increasing benefits could significantly impact the federal budget. However, proponents argue that the long-term benefits, such as improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs, can offset these initial costs.
Another consideration is the potential for fraud and abuse. While SNAP has robust measures in place to prevent fraud, increasing benefits could attract unscrupulous individuals who may attempt to exploit the system. Ongoing efforts to strengthen program integrity are essential to ensure that SNAP benefits reach those who truly need them.
Future Implications and Policy Recommendations

The ongoing debate around SNAP benefit increases highlights the program’s critical role in addressing food insecurity and promoting nutritional well-being. As policymakers continue to shape the future of SNAP, several key considerations and recommendations emerge.
Evidence-Based Decision Making
Policy decisions regarding SNAP benefits should be guided by robust research and evidence. Studies have shown that increasing SNAP benefits can lead to tangible improvements in food security and dietary quality. By investing in research and data collection, policymakers can make informed decisions that maximize the program’s impact.
Targeted Benefit Increases
While increasing SNAP benefits overall can have significant benefits, targeted increases for specific populations may be even more effective. For example, providing additional benefits to households with children, the elderly, or individuals with disabilities could help address the unique nutritional needs of these vulnerable groups.
Nutrition Education and Support
In conjunction with benefit increases, providing nutrition education and support to SNAP recipients can further enhance the program’s effectiveness. This could include initiatives to promote healthy eating habits, such as cooking classes, nutrition workshops, and community gardens. By empowering SNAP recipients with the knowledge and skills to make healthy food choices, the program can have a lasting impact on dietary habits.
Addressing Administrative Barriers
Ensuring that eligible individuals can easily access SNAP benefits is crucial. Simplifying the application process, reducing paperwork, and improving outreach efforts can help reduce administrative barriers and ensure that those in need receive the support they deserve.
Collaborative Efforts
Addressing food insecurity and promoting healthy diets requires a collaborative approach involving various stakeholders, including government agencies, community organizations, and the private sector. By working together, these entities can leverage their unique strengths and resources to develop innovative solutions and ensure that SNAP benefits are used effectively to improve nutritional outcomes.
What is the current average monthly SNAP benefit per person?
+The average monthly SNAP benefit per person is approximately 121.00.</p> </div> </div> <div class="faq-item"> <div class="faq-question"> <h3>How much does the SNAP Emergency Benefit provide per person per month?</h3> <span class="faq-toggle">+</span> </div> <div class="faq-answer"> <p>The SNAP Emergency Benefit provides an additional 20.00 per person per month.
What is the proposed increase in SNAP benefits by Senator Bernie Sanders and Representative Ilhan Omar?
+Senator Bernie Sanders and Representative Ilhan Omar propose to double SNAP benefits and eliminate the asset test for eligibility.



