Nuttall Oak Tree
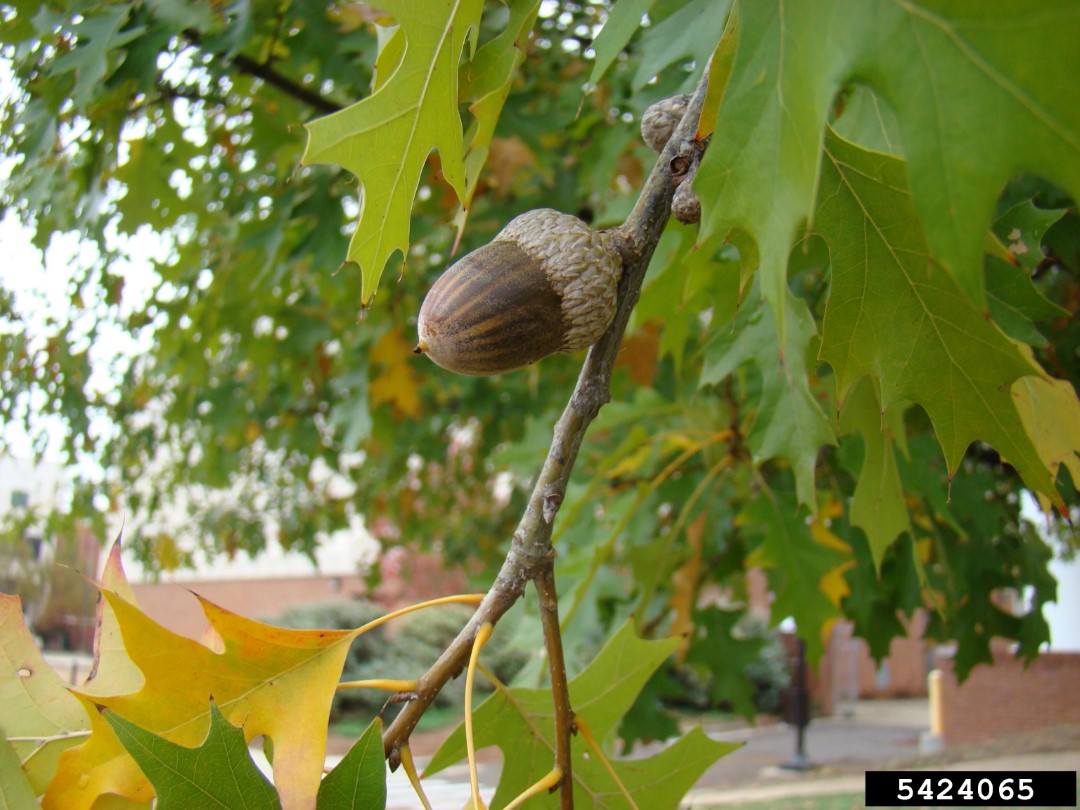

The Nuttall Oak, scientifically known as Quercus nuttallii, is a majestic and resilient tree species native to the southern United States. With its impressive size, longevity, and ecological significance, this oak tree has become an iconic symbol of strength and endurance in the regions it inhabits. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of the Nuttall Oak, exploring its characteristics, growth patterns, ecological role, and the cultural significance it holds.
Botanical Characteristics and Taxonomy
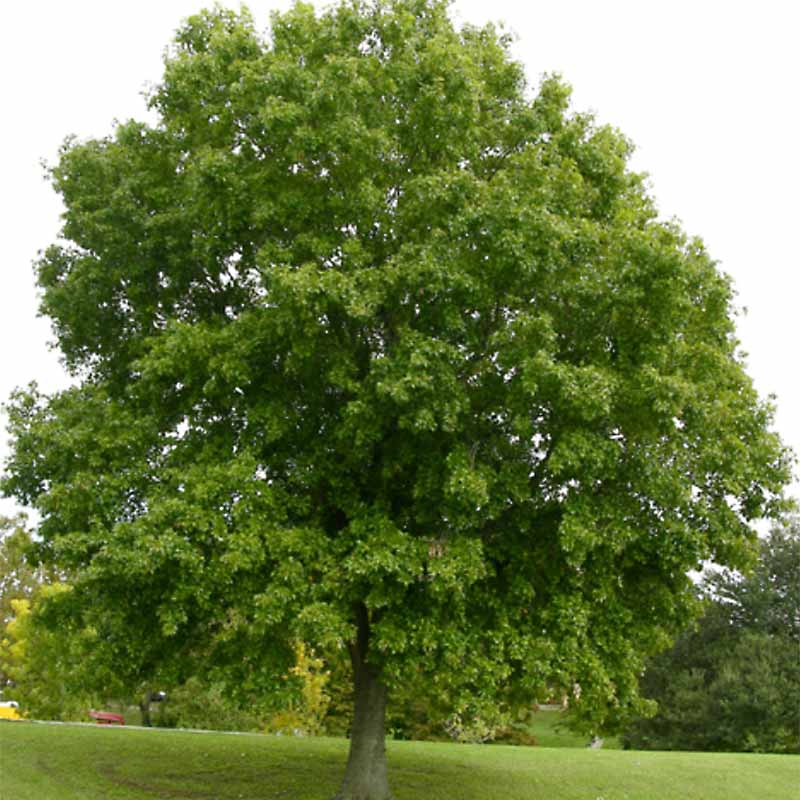

The Nuttall Oak belongs to the Fagaceae family, which includes various oak, beech, and chestnut species. It is named after the English botanist and explorer Thomas Nuttall, who made significant contributions to the study of North American flora. This deciduous tree is known for its robust growth and ability to thrive in diverse environmental conditions.
Physical Description
The Nuttall Oak can reach impressive heights, often growing up to 80 feet (24 meters) tall, with some specimens surpassing 100 feet (30 meters). Its trunk is sturdy and can measure up to 3 feet (1 meter) in diameter. The bark is grayish-brown and deeply furrowed, adding to the tree’s distinctive appearance. The leaves are elliptical, with a glossy green color on the upper surface and a lighter shade on the underside. They have a slightly toothed margin and can grow up to 6 inches (15 cm) long.
Reproductive Characteristics
Like other oak trees, the Nuttall Oak is monoecious, meaning it bears both male and female flowers on the same tree. The male flowers, or catkins, are long and pendulous, while the female flowers are small and inconspicuous. The acorns, which are the fruit of the tree, take two years to mature. They are about 1 inch (2.5 cm) long, with a shallow, saucer-shaped cap that covers about a quarter of the nut. The acorns provide a valuable food source for various wildlife, including birds, squirrels, and deer.
Habitat and Distribution
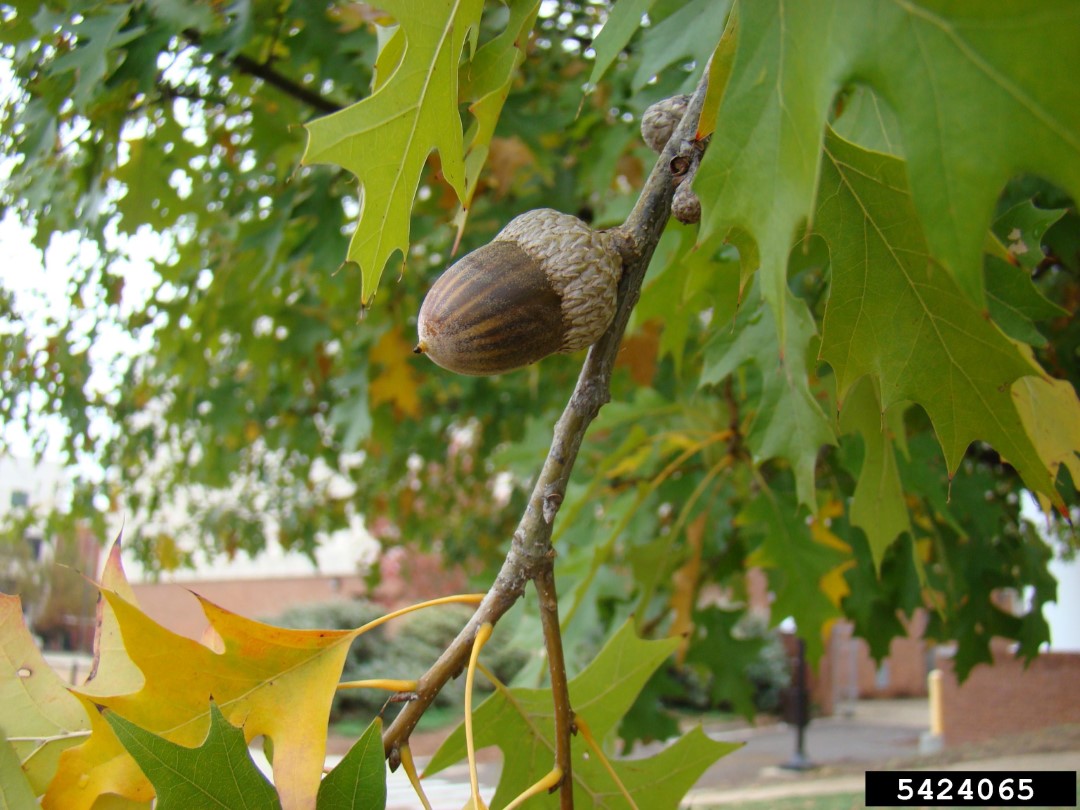

The Nuttall Oak is native to the southeastern United States, primarily found in the states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including bottomland forests, floodplains, and riverbanks. This oak species is well-adapted to both wet and dry soil conditions, making it a versatile and resilient tree.
Ecological Role
The Nuttall Oak plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. Its dense canopy provides shade and habitat for a diverse range of wildlife. The acorns, as mentioned earlier, are a vital food source for many animals, contributing to the overall health and balance of the ecosystem. Additionally, the tree’s extensive root system helps prevent soil erosion, particularly along riverbanks and in flood-prone areas.
| Habitat | Adaptability |
|---|---|
| Bottomland Forests | Highly Adaptable |
| Floodplains | Tolerant of Wet Conditions |
| Riverbanks | Resistant to Flooding |

Growth and Cultivation

The Nuttall Oak is a relatively fast-growing tree, especially when compared to other oak species. It can grow at a rate of 24 inches (60 cm) or more per year under optimal conditions. The tree prefers full sun to partial shade and well-drained soil. While it can tolerate occasional flooding, it does not thrive in constantly wet conditions.
Propagation and Seedling Development
Propagation of the Nuttall Oak is typically achieved through seed germination. The acorns can be collected and stored in a cool, dry place until ready for planting. They require a period of cold stratification to break dormancy and initiate germination. Once planted, the seedlings grow rapidly, with a vigorous taproot system developing in the first year.
Cultivar Selection
Various cultivars of the Nuttall Oak have been developed to enhance specific characteristics. Some popular cultivars include:
- Quercus nuttallii 'Prairie Dawn': Known for its rapid growth and resistance to oak wilt disease.
- Quercus nuttallii 'Splendens': Showcases vibrant fall foliage with shades of red and orange.
- Quercus nuttallii 'Bowman': A compact variety suitable for smaller landscapes, with a more rounded crown.
Cultural Significance and Uses

The Nuttall Oak holds cultural and historical significance in the regions it inhabits. Native American tribes, such as the Choctaw and Cherokee, utilized the tree for various purposes, including constructing dwellings and crafting tools. The acorns were also a valuable food source, often ground into flour or used as a coffee substitute.
Ornamental Value
In modern times, the Nuttall Oak is widely cultivated as an ornamental tree. Its impressive size, attractive foliage, and ability to provide shade make it a popular choice for parks, gardens, and urban landscapes. The tree’s tolerance to air pollution and urban conditions makes it well-suited for street plantings and green spaces in cities.
Timber and Woodworking
The wood of the Nuttall Oak is highly valued for its strength and durability. It is commonly used in construction, furniture making, and flooring. The heartwood, which is a reddish-brown color, is particularly resistant to decay and insect damage, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
Challenges and Conservation

Despite its resilience, the Nuttall Oak faces several challenges in its natural habitat. Urbanization and land development have led to the loss of its native range, while diseases such as oak wilt and insect infestations pose additional threats. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the long-term survival of this iconic tree species.
Conservation Initiatives
Several organizations and initiatives are dedicated to the conservation and restoration of the Nuttall Oak and its habitat. These efforts include:
- The Nuttall Oak Conservation Project, which focuses on research, education, and habitat restoration.
- The Nature Conservancy has established reserves and conservation areas to protect the tree's natural habitat.
- Local community groups and arboretums often participate in tree-planting initiatives to increase the population of Nuttall Oaks.
What are the ideal soil conditions for growing Nuttall Oak trees?
+Nuttall Oak trees thrive in well-drained soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 7.5. They can tolerate a variety of soil types, including sandy, loamy, and clay soils, but prefer slightly acidic to neutral conditions. Proper soil drainage is crucial to prevent root rot and other fungal diseases.
How long does it take for a Nuttall Oak to reach maturity?
+Nuttall Oaks typically reach maturity within 30 to 40 years. However, with optimal growing conditions and proper care, they can grow faster and reach maturity in as little as 20 years.
Are Nuttall Oaks susceptible to any specific pests or diseases?
+While Nuttall Oaks are generally hardy, they can be affected by certain pests and diseases. Common issues include oak wilt, caused by a fungus, and insect infestations such as oak leaf rollers and oak scale. Regular monitoring and appropriate pest management practices are essential to maintain the health of these trees.
In conclusion, the Nuttall Oak is a remarkable tree species, renowned for its beauty, strength, and ecological importance. Its ability to adapt to various conditions and provide valuable resources makes it a vital component of its ecosystem. Through conservation efforts and responsible cultivation, we can ensure the continued presence of this iconic tree for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.