Nutritional Info Chicken Thighs
Chicken thighs are a popular cut of poultry meat known for their rich flavor and tender texture. They are a versatile ingredient used in various cuisines and cooking methods, offering a nutritious and flavorful addition to meals. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the nutritional content of chicken thighs, exploring their macro and micronutrient profiles, health benefits, and potential considerations for a balanced diet.
Macro and Micronutrient Composition

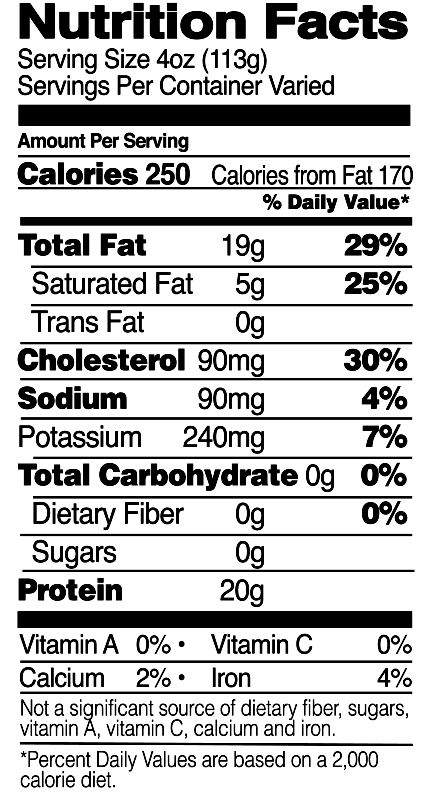
Chicken thighs are a nutrient-dense food, offering a range of essential macro and micronutrients. The following is a detailed breakdown of their nutritional composition:
Protein
Chicken thighs are an excellent source of high-quality protein. A 100-gram serving of cooked chicken thighs provides approximately 26 grams of protein, which is essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall body maintenance. The protein in chicken thighs contains all the essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source.
Fat
Chicken thighs are relatively higher in fat content compared to other cuts of chicken, such as breast meat. A 100-gram serving contains around 13 grams of fat, with a significant portion being monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These healthy fats contribute to heart health and provide essential fatty acids, such as omega-3 and omega-6.
Carbohydrates
Chicken thighs are very low in carbohydrates, with less than 1 gram per 100-gram serving. This makes them an ideal choice for low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diets, as they provide a satisfying source of protein and fat without adding significant carbohydrates.
Vitamins and Minerals
Chicken thighs are a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Essential for energy production and maintaining healthy skin.
- Vitamin B6: Important for brain function and the production of neurotransmitters.
- Vitamin B12: Vital for red blood cell formation and nerve function.
- Iron: Necessary for oxygen transport and energy metabolism.
- Zinc: Plays a role in immune function and wound healing.
- Selenium: An antioxidant that supports thyroid function and immune health.
Health Benefits of Chicken Thighs

Incorporating chicken thighs into a balanced diet can offer several health benefits, including:
Heart Health
The monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in chicken thighs can help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. These healthy fats also promote the production of HDL (“good”) cholesterol, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Muscle and Tissue Repair
The high protein content of chicken thighs makes them an excellent choice for muscle growth and repair. Protein is essential for building and maintaining lean muscle mass, making chicken thighs a valuable addition to a post-workout meal or a protein-rich snack.
Immune System Support
The vitamins and minerals present in chicken thighs, such as vitamin B6, B12, iron, and zinc, play crucial roles in supporting a healthy immune system. Adequate intake of these nutrients can help strengthen the body’s defense mechanisms and reduce the risk of infections.
Brain Health
Vitamin B6 and B12, found in chicken thighs, are essential for brain function and the production of neurotransmitters. These vitamins contribute to cognitive health, memory, and overall brain performance.
Potential Considerations

While chicken thighs offer numerous nutritional benefits, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
Saturated Fat
Chicken thighs contain a higher proportion of saturated fat compared to other cuts of chicken. While saturated fat is essential for certain bodily functions, excessive intake can increase LDL cholesterol levels and potentially contribute to heart disease. It is important to consume chicken thighs in moderation and balance them with other lean protein sources.
Caloric Intake
Due to their higher fat content, chicken thighs are more calorie-dense than other cuts of chicken. A 100-gram serving contains approximately 210 calories. Individuals monitoring their calorie intake should be mindful of portion sizes to ensure they align with their dietary goals.
Food Safety
Proper handling and cooking of chicken thighs are crucial to prevent foodborne illnesses. It is essential to cook chicken thighs thoroughly to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to ensure any harmful bacteria are eliminated. Storing and handling raw chicken properly can also minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
Nutritional Comparison with Other Cuts of Chicken

Comparing the nutritional profile of chicken thighs with other popular cuts of chicken, such as breast and drumsticks, provides a comprehensive understanding of their relative benefits:
| Nutrient | Chicken Thighs | Chicken Breast | Chicken Drumsticks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (g) | 26 | 31 | 23 |
| Fat (g) | 13 | 3 | 12 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vitamin B3 (mg) | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.3 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Vitamin B12 (μg) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Iron (mg) | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| Zinc (mg) | 3.4 | 2.4 | 2.8 |

As the table illustrates, chicken thighs offer a higher fat content and a slightly lower protein content compared to chicken breast. However, they provide similar levels of vitamins and minerals. Chicken drumsticks have a nutritional profile similar to thighs, with slightly lower protein and higher fat content.
Incorporating Chicken Thighs into a Balanced Diet
Chicken thighs can be a valuable addition to a well-rounded diet. Here are some tips for incorporating them into meals:
- Choose leaner cuts of chicken thighs, such as those with less visible fat.
- Pair chicken thighs with a variety of vegetables to increase nutrient intake and fiber content.
- Experiment with different cooking methods, such as grilling, baking, or stir-frying, to enhance flavor and texture.
- Use chicken thighs as a base for hearty soups, stews, or curries, adding a boost of protein and flavor.
- Consider marinating chicken thighs to add moisture and enhance their taste.
Are chicken thighs a healthier option than chicken breast?
+Chicken thighs and breasts have different nutritional profiles. Chicken thighs are higher in fat and calories but also offer more flavor and moisture. Chicken breast is leaner and lower in fat but may require more careful cooking to avoid dryness. Ultimately, both can be healthy options when consumed in moderation and prepared healthily.
Can chicken thighs be part of a weight-loss diet?
+Yes, chicken thighs can be included in a weight-loss diet. While they are higher in fat and calories compared to other cuts of chicken, their high protein content can help promote satiety and support muscle maintenance during weight loss. It is important to control portion sizes and pair them with low-calorie, nutrient-dense foods.
Are there any specific cooking methods recommended for chicken thighs?
+Chicken thighs can be cooked using various methods, including baking, grilling, roasting, and stir-frying. Baking and roasting can help retain moisture and enhance flavor, while grilling can add a smoky taste. Stir-frying is a quick and convenient method, especially when paired with vegetables. The choice of cooking method depends on personal preference and the desired texture and flavor.


