Natural Pest Control: A Comprehensive Guide To Ecofriendly Solutions

Natural pest control is an increasingly popular and sustainable approach to managing pests in various environments, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical-based methods. This comprehensive guide explores the principles, techniques, and benefits of adopting natural pest control strategies, highlighting their importance in modern agriculture, horticulture, and urban pest management.
Understanding Natural Pest Control

Natural pest control, often referred to as biological pest control, utilizes the principles of ecology and the natural interactions between organisms to manage pest populations. It is a holistic approach that aims to maintain a balanced ecosystem where pests are controlled by their natural predators, parasites, or pathogens, without the use of synthetic chemicals.
This method of pest control has gained prominence due to the growing awareness of the environmental and health risks associated with chemical pesticides. Natural pest control not only reduces the negative impacts on the environment and human health but also promotes the long-term sustainability of agricultural and urban ecosystems.
The Principles of Natural Pest Control
The core principles of natural pest control revolve around understanding the ecology of pests and their natural enemies. It involves creating an environment that fosters the survival and proliferation of beneficial organisms while suppressing the growth and reproduction of pests.
- Conservation of Natural Enemies: Natural enemies, such as predators and parasites, play a crucial role in controlling pest populations. Natural pest control strategies focus on preserving and enhancing the populations of these beneficial organisms.
- Habitat Modification: Altering the habitat to make it less favorable for pests is a key aspect of natural pest control. This can involve simple practices like crop rotation, intercropping, and the use of physical barriers to deter pests.
- Biological Control Agents: In some cases, introducing specific biological control agents, such as beneficial insects or microorganisms, can help suppress pest populations. These agents are carefully selected to target specific pests without causing harm to non-target organisms.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Natural pest control is often integrated into IPM strategies, which combine various control methods, including cultural, biological, and chemical approaches, to manage pests effectively and sustainably.
Techniques for Natural Pest Control

Natural pest control encompasses a wide range of techniques and strategies, each tailored to specific pest problems and environmental conditions. Here are some of the most effective and commonly used techniques:
1. Conservation and Augmentation of Natural Enemies
Natural enemies, including predators, parasites, and pathogens, are vital in controlling pest populations. Conservation of these natural enemies involves creating favorable habitats and providing food sources to support their populations.
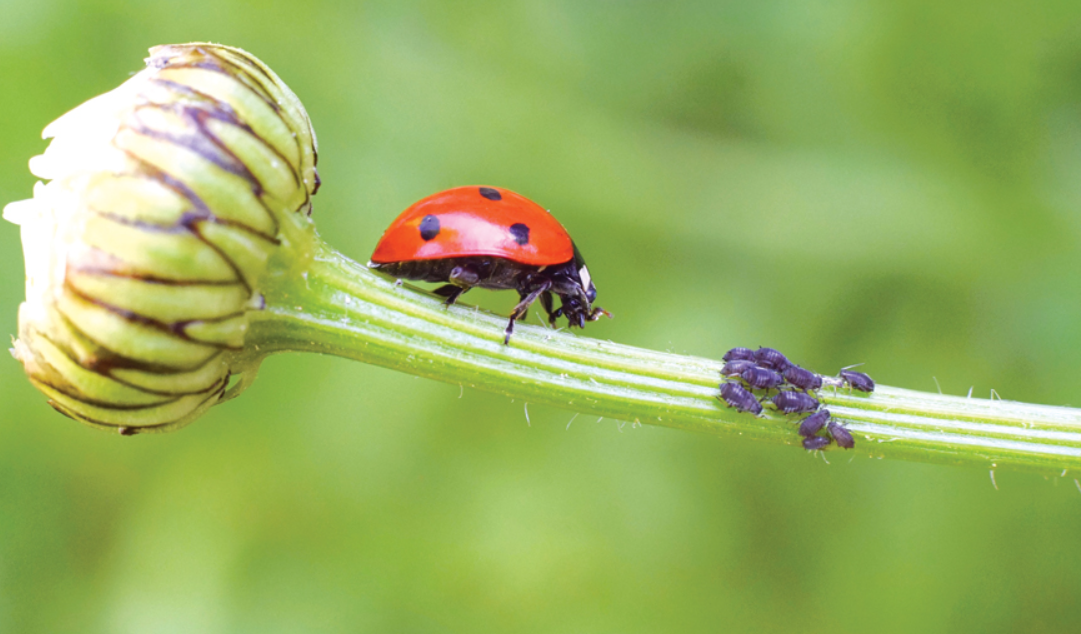
For example, planting flowers and herbs that attract beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps, can help control aphids, caterpillars, and other pests. Similarly, providing shelter and water sources can encourage the presence of birds and bats, which are natural predators of insects.
2. Habitat Modification
Modifying the habitat to make it less attractive to pests is a key strategy in natural pest control. This can involve:
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops helps disrupt the life cycles of pests that are specific to certain plants. It also helps to reduce the buildup of pests in the soil.
- Intercropping: Planting different crops in close proximity can confuse pests and make it difficult for them to locate their preferred host plants.
- Physical Barriers: Using physical barriers, such as nets, screens, or fences, can prevent pests from accessing crops or vulnerable areas.
- Sanitation and Hygiene: Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment can reduce pest attractants and breeding sites. Proper waste management and regular cleaning can help prevent pest infestations.
3. Biological Control Agents
In certain cases, introducing specific biological control agents can be an effective strategy. These agents are carefully selected to target specific pests and are often used in conjunction with other natural pest control methods.
For instance, the use of parasitic wasps to control caterpillar populations in agricultural settings is a common biological control approach. These wasps lay their eggs inside the caterpillars, eventually killing them as the wasp larvae develop.
4. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM is a holistic approach to pest management that integrates various control methods, including natural pest control techniques. IPM focuses on understanding the ecology of pests and their interactions with the environment to develop sustainable and effective control strategies.
IPM strategies often involve regular monitoring and scouting to identify pest problems early on. This allows for the implementation of targeted control measures, such as the release of natural enemies or the use of pheromone traps, before pest populations reach damaging levels.
Benefits of Natural Pest Control

Adopting natural pest control strategies offers a multitude of benefits, both for the environment and for human health. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Environmental Sustainability
Natural pest control promotes the long-term sustainability of ecosystems by minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals. This reduces the risk of chemical runoff into water bodies, soil contamination, and the accumulation of pesticides in the food chain.
By preserving and enhancing the populations of natural enemies, natural pest control helps maintain a balanced ecosystem. This approach also encourages biodiversity, as it supports the survival of a wide range of organisms, including beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife.
2. Human Health and Safety
Chemical pesticides can pose risks to human health, especially when used indiscriminately or in large quantities. Natural pest control methods eliminate or significantly reduce the use of these chemicals, thereby minimizing potential health hazards for farmers, workers, and consumers.
Additionally, natural pest control strategies often focus on prevention and early intervention, reducing the need for reactive, chemical-intensive control measures. This approach helps to create a safer and healthier environment for all.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial implementation of natural pest control strategies may require investment in education and infrastructure, it can lead to long-term cost savings. Natural pest control methods are often more cost-effective than chemical control in the long run, as they reduce the need for frequent pesticide applications and minimize the risk of pest resistance.
Furthermore, natural pest control can enhance the overall health and productivity of crops, leading to higher yields and better-quality produce. This can result in increased profitability for farmers and reduced food costs for consumers.
4. Regulatory Compliance
With increasing concerns about the environmental and health impacts of chemical pesticides, many regulatory bodies are encouraging or mandating the adoption of more sustainable pest control practices. Natural pest control strategies align with these regulatory trends, helping farmers and businesses stay compliant and avoid potential legal and reputational risks.
Challenges and Limitations

While natural pest control offers numerous benefits, it also comes with certain challenges and limitations that must be considered:
1. Time and Labor Intensive
Natural pest control strategies often require more time and labor compared to chemical control methods. Implementing habitat modifications, conservation of natural enemies, and regular monitoring can be time-consuming and labor-intensive tasks.
2. Knowledge and Expertise
Successful natural pest control relies on a deep understanding of pest ecology and the interactions between pests and their natural enemies. Farmers, growers, and pest management professionals need access to education and training to effectively implement these strategies.
3. Limited Control of Certain Pests
While natural pest control can be highly effective for many pests, it may not provide complete control for all pest species. Some pests, especially those with complex life cycles or those that are highly mobile, may require additional control measures or a combination of strategies.
4. Weather and Environmental Factors
Natural pest control strategies can be influenced by weather conditions and other environmental factors. Extreme weather events, such as droughts or heavy rainfall, can impact the effectiveness of natural enemies and the success of habitat modifications.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Natural Pest Control

Natural pest control has been successfully implemented in various agricultural and urban settings, demonstrating its effectiveness and potential for wide-scale adoption. Here are a few notable case studies:
1. Integrated Pest Management in California’s Vineyards
In California’s wine-growing regions, integrated pest management (IPM) has been successfully employed to control pests while minimizing the use of chemical pesticides. By combining natural pest control techniques, such as the release of predatory mites and the use of pheromone traps, with cultural practices like crop rotation and habitat modification, vineyards have been able to reduce pesticide use by up to 75% while maintaining high-quality wine production.
2. Biological Control of Mosquitoes in Urban Areas
In many urban areas, the use of biological control agents, such as mosquito fish and Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), has proven effective in controlling mosquito populations. These natural control methods reduce the need for chemical insecticides and help prevent the spread of mosquito-borne diseases, such as West Nile virus and Zika virus.
3. Organic Agriculture and Natural Pest Control
Organic agriculture relies heavily on natural pest control strategies to maintain the integrity of the organic certification. Organic farmers use a combination of techniques, including crop rotation, intercropping, and the conservation of natural enemies, to control pests while adhering to strict organic standards.
Future Perspectives and Innovations

The field of natural pest control is continually evolving, with ongoing research and innovation leading to new and improved strategies. Here are some future perspectives and potential developments:
1. Precision Agriculture and Pest Control
Advancements in precision agriculture technologies, such as remote sensing and data analytics, can enhance the effectiveness of natural pest control. These technologies can help farmers identify pest hotspots, monitor pest populations, and make data-driven decisions about the implementation of natural control measures.
2. Genetic Engineering and Biocontrol
Genetic engineering techniques may offer new opportunities for developing biological control agents. By modifying the genetic makeup of certain organisms, scientists can create more effective and targeted control agents that can be used in natural pest control strategies.
3. Urban Agriculture and Natural Pest Control
With the growing interest in urban agriculture and rooftop farming, natural pest control strategies are becoming increasingly important in these settings. Urban farmers can employ techniques such as companion planting, habitat modification, and the use of beneficial insects to control pests without relying on chemical pesticides.
4. Education and Outreach
Widespread adoption of natural pest control strategies requires education and outreach efforts to raise awareness among farmers, growers, and the general public. Providing accessible information and resources can help empower individuals to make informed choices about pest management and contribute to a more sustainable future.
How can I get started with natural pest control in my garden or farm?
+Starting with natural pest control requires a holistic approach. Begin by understanding the ecology of your garden or farm, including the common pests and their natural enemies. Implement habitat modifications, such as crop rotation and intercropping, to disrupt pest life cycles. Consider introducing or conserving natural enemies, such as beneficial insects or birds, to control pest populations. Regular monitoring and scouting are essential to identify pest problems early on and implement targeted control measures. Remember that natural pest control is a learning process, and seeking guidance from local agricultural extension services or experienced farmers can be beneficial.
Are there any natural pest control methods for specific pests, such as aphids or caterpillars?
+Yes, natural pest control offers a range of targeted strategies for specific pests. For aphids, planting flowers that attract aphid predators, such as ladybugs and lacewings, can help control their populations. Similarly, for caterpillars, introducing or conserving parasitic wasps or releasing specific biological control agents can be effective. It’s important to research and understand the specific life cycles and natural enemies of the pests you’re targeting to develop an effective natural control strategy.
How can I find resources and support for implementing natural pest control practices?
+There are various resources available to support the implementation of natural pest control practices. Local agricultural extension services often provide guidance and training on sustainable pest management. Online platforms and communities dedicated to organic farming and natural pest control can also offer valuable insights and support. Additionally, seeking advice from experienced farmers or attending workshops and seminars on natural pest control can be beneficial.