Monarch Butterfly Caterpillars: A Guide To Their Remarkable Transformation
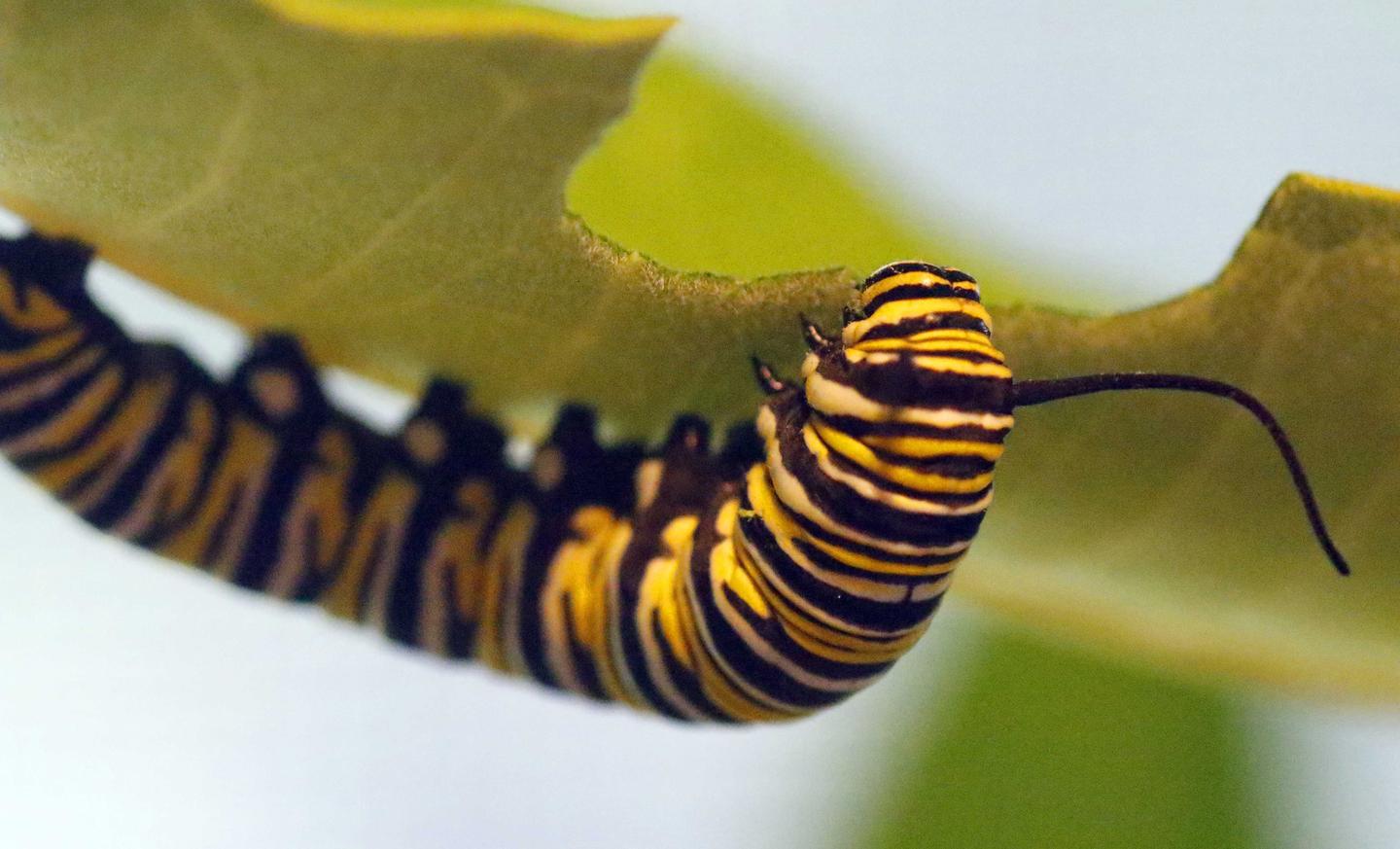

The metamorphosis of a Monarch butterfly caterpillar into a breathtaking adult butterfly is a truly remarkable process. This intricate journey, from a tiny egg to a magnificent winged creature, has captivated naturalists and enthusiasts alike. Let's delve into the world of Monarch caterpillars, exploring their unique life cycle, remarkable adaptations, and the crucial role they play in the ecosystem.
The Life Cycle of a Monarch Butterfly Caterpillar

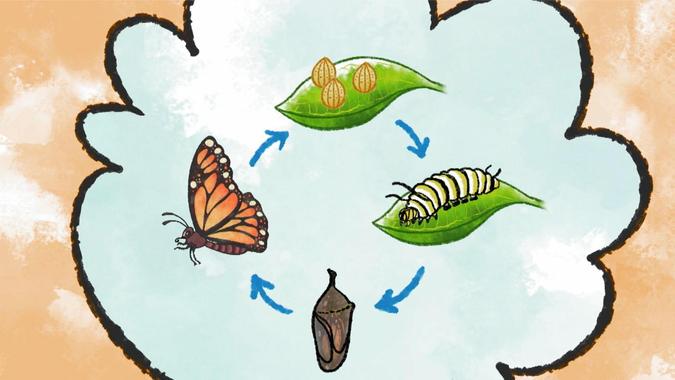
The life of a Monarch butterfly begins with a single egg, carefully laid by the female butterfly on the underside of a milkweed leaf. These eggs are a mere 1.2 mm in length, yet they hold the potential for an incredible transformation. After approximately 3 to 8 days, depending on environmental conditions, the egg hatches, revealing a tiny, newly hatched caterpillar, or larva.
The Larval Stage
The larval stage is a period of rapid growth and development for the Monarch caterpillar. During this phase, which typically lasts around 2 to 3 weeks, the caterpillar undergoes several molts, shedding its exoskeleton as it grows. Each molt results in a larger, more developed caterpillar, with distinctive yellow, black, and white stripes running along its body.
Monarch caterpillars are voracious eaters, consuming an impressive amount of milkweed leaves. In fact, they are known to consume approximately 20 times their body weight in food during this stage! This diet is crucial, as milkweed contains a toxin that makes the caterpillars unpalatable to predators, offering them a natural defense mechanism.
Pupal Stage: The Transformation Begins
As the caterpillar reaches the end of its larval stage, it begins to search for a suitable location to begin its transformation into a butterfly. It typically selects a protected spot, such as the underside of a leaf or a twig, where it spins a silk pad and attaches itself, forming a “J” shape. After a period of rest, the caterpillar sheds its skin for the final time, revealing a green, gold-speckled chrysalis.
Within the chrysalis, an incredible transformation takes place. The caterpillar's body breaks down and reorganizes, forming the intricate structures of a butterfly. This process, known as metamorphosis, is a true marvel of nature. After approximately 10 to 14 days, the chrysalis becomes transparent, indicating that the transformation is nearly complete.
Emergence of the Adult Butterfly
Finally, the moment of truth arrives. The adult Monarch butterfly emerges from the chrysalis, its wings initially wet and crumpled. It quickly pumps fluid from its body into the veins of its wings, expanding them to their full size. As the wings dry and harden, the butterfly takes its first flight, a true testament to the power of nature’s design.
The entire life cycle of a Monarch butterfly, from egg to adult, typically takes around 30 to 45 days, depending on environmental conditions. This remarkable journey is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of these incredible creatures.
Adaptations and Survival Strategies
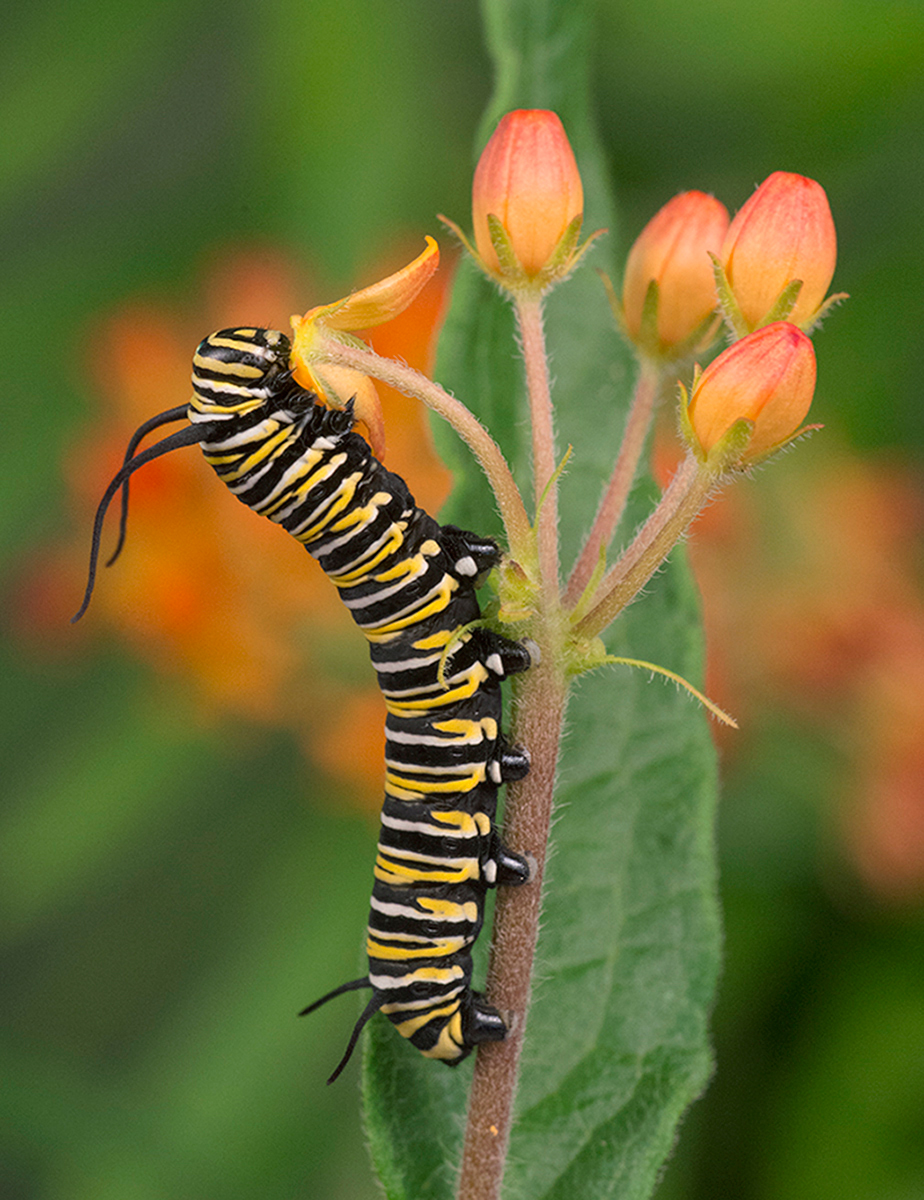
Monarch butterfly caterpillars have evolved a range of adaptations and survival strategies to ensure their survival in a world filled with predators and environmental challenges.
Camouflage and Warning Colors
The distinctive yellow, black, and white stripes of the Monarch caterpillar serve a dual purpose. Firstly, they provide effective camouflage, allowing the caterpillar to blend in with the veins of milkweed leaves, making it difficult for predators to spot. Secondly, these colors act as a warning signal to potential predators, indicating that the caterpillar is toxic and unpalatable.
Chemical Defense
Monarch caterpillars derive their toxicity from the milkweed plants they feed on. Milkweed contains cardiac glycosides, which are toxic to many animals. When a Monarch caterpillar consumes milkweed, it incorporates these toxins into its body, making it unappetizing to predators. This chemical defense mechanism is a powerful tool for survival.
Migration and Overwintering
One of the most remarkable aspects of Monarch butterflies is their annual migration. Monarchs that breed in the northern United States and Canada embark on a journey south, traveling thousands of miles to reach their overwintering sites in Mexico and California. This migration ensures their survival during the cold winter months.
During the migration, Monarchs form large clusters on trees, often in the millions, creating a breathtaking spectacle. These clusters provide protection from the cold and serve as a vital energy reserve for the butterflies as they await the arrival of spring.
Ecological Significance

Monarch butterflies, and their caterpillar stage, play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They are considered a keystone species, meaning their presence or absence can have a significant impact on the entire ecosystem.
Pollination
Adult Monarch butterflies are important pollinators, contributing to the reproduction of a wide range of flowering plants. As they feed on nectar, they transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the process of pollination. This, in turn, ensures the production of fruits and seeds, which are vital for the survival of many plant species.
Ecosystem Balance
The presence of Monarch caterpillars helps to maintain a balance in the ecosystem. By feeding on milkweed, they control the growth of these plants, preventing them from becoming overly dominant. Additionally, their presence provides a food source for a variety of predators, including birds, insects, and small mammals, contributing to the overall health and diversity of the ecosystem.
Indicator Species
Monarch butterflies are often referred to as an indicator species, meaning their population health can provide insights into the overall health of the ecosystem. A decline in Monarch populations can indicate environmental stressors, such as habitat loss, climate change, or the use of pesticides. Monitoring Monarch populations can, therefore, serve as an early warning system for potential ecological issues.
Conservation and Threats

Despite their remarkable resilience and adaptability, Monarch butterflies face a range of threats that have led to a decline in their populations. Understanding and addressing these threats is crucial for the long-term survival of these iconic creatures.
Habitat Loss
One of the primary threats to Monarch butterflies is the loss of their habitat. The conversion of natural areas into agricultural land, urban development, and the use of herbicides have led to a significant reduction in milkweed populations, the sole food source for Monarch caterpillars. Without sufficient milkweed, Monarchs struggle to find suitable breeding grounds, leading to a decline in their numbers.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant challenge to Monarch butterflies. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can disrupt the delicate timing of their migration and breeding cycles. Additionally, extreme weather events, such as droughts and storms, can impact the availability of milkweed and nectar sources, further threatening their survival.
Pesticide Use
The use of pesticides, particularly in agricultural areas, can have detrimental effects on Monarch butterflies. Pesticides can directly harm Monarchs by poisoning them, or they can indirectly impact their survival by reducing the availability of milkweed and nectar sources. The use of neonicotinoid pesticides, in particular, has been linked to declines in Monarch populations.
Conservation Efforts

Recognizing the importance of Monarch butterflies and the threats they face, conservation efforts have been implemented to protect and restore their populations.
Habitat Restoration
Efforts are underway to restore and protect Monarch habitat, particularly milkweed populations. Conservation organizations, government agencies, and individuals are working together to plant milkweed in gardens, along roadsides, and in other suitable areas. This helps to provide a food source for Monarch caterpillars and breeding grounds for adult butterflies.
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the importance of Monarch butterflies and the threats they face is a crucial aspect of conservation. Educational programs, outreach initiatives, and public engagement campaigns help to inform people about the role of Monarchs in the ecosystem and the actions they can take to support their survival.
Research and Monitoring
Ongoing research and monitoring of Monarch populations are essential for understanding their needs and the effectiveness of conservation efforts. Scientists and citizen scientists collaborate to track Monarch migration routes, monitor population sizes, and study the impacts of various factors on their survival. This data-driven approach helps to guide conservation strategies and ensure their success.
How long does the entire life cycle of a Monarch butterfly take?
+The entire life cycle of a Monarch butterfly, from egg to adult, typically takes around 30 to 45 days, depending on environmental conditions. This remarkable journey showcases the resilience and adaptability of these iconic creatures.
What is the role of milkweed in the life of a Monarch butterfly?
+Milkweed is the sole food source for Monarch caterpillars. It provides the necessary nutrients for their growth and development, and it also contains toxins that make the caterpillars unpalatable to predators, offering them a natural defense mechanism.
Why are Monarch butterflies considered a keystone species?
+Monarch butterflies are considered a keystone species because their presence or absence can have a significant impact on the entire ecosystem. They play a crucial role in pollination, ecosystem balance, and as an indicator species, providing insights into the overall health of the environment.
What are the main threats facing Monarch butterflies?
+Monarch butterflies face a range of threats, including habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use. The loss of milkweed habitat, rising temperatures, and the use of pesticides all contribute to the decline in Monarch populations, highlighting the need for conservation efforts.
How can individuals contribute to Monarch conservation?
+Individuals can contribute to Monarch conservation by planting milkweed in their gardens, avoiding the use of pesticides, and supporting conservation organizations. Additionally, participating in citizen science projects and spreading awareness about the importance of Monarchs can make a significant impact.

