Helene Hurricane Map: Track Its Path & Stay Prepared
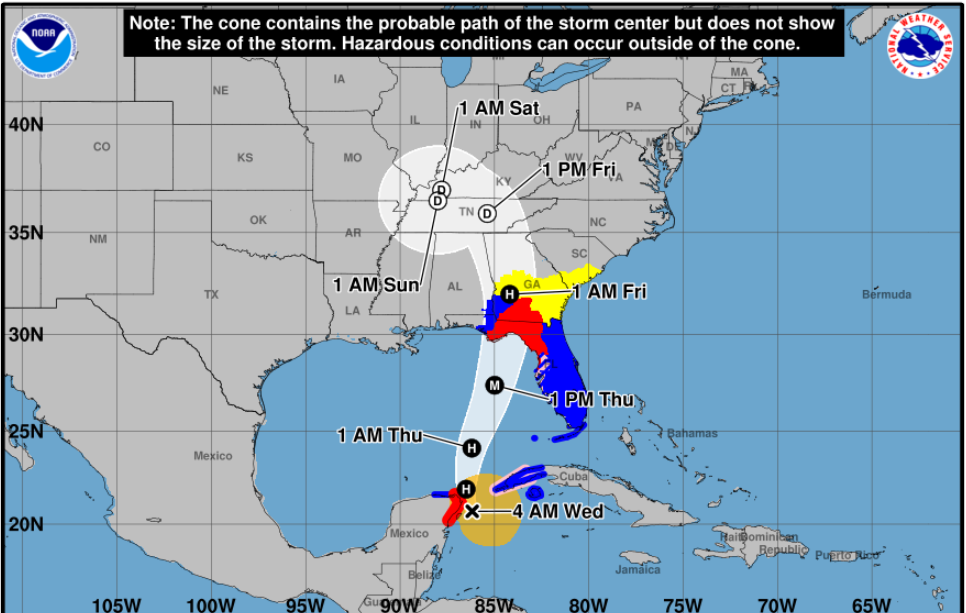
Hurricane Helene is a powerful and potentially devastating tropical cyclone that formed in the Atlantic Ocean during the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season. This category 2 hurricane, with its intense winds and heavy rainfall, posed a significant threat to coastal regions and required meticulous tracking and preparedness measures.
Hurricane Helene’s Formation and Early Track
Hurricane Helene originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the west coast of Africa on September 6, 2018. As it moved westward across the Atlantic, favorable environmental conditions, including warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear, allowed the system to rapidly intensify. On September 8, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) classified the system as Tropical Depression Eight, and it was subsequently upgraded to Tropical Storm Helene later that day.
Over the following days, Helene continued to strengthen as it moved westward, with its maximum sustained winds reaching 70 mph (110 km/h). On September 10, the NHC reported that Helene had intensified into a hurricane, with maximum sustained winds of 75 mph (120 km/h). At this point, the hurricane was located approximately 1,050 miles (1,690 km) west-southwest of the southernmost Cape Verde Islands.
Intensification and Peak Strength
As Helene continued its westward journey, it encountered even more favorable conditions, allowing it to rapidly intensify. On September 11, the hurricane’s maximum sustained winds increased to 100 mph (160 km/h), categorizing it as a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. At its peak, Helene’s minimum central pressure dropped to 974 millibars, indicating a powerful and well-organized storm system.
During this period, Helene maintained a steady westward track, posing a potential threat to the Lesser Antilles and the Caribbean. However, as it moved further west, it began to encounter slightly less favorable conditions, including slightly cooler sea surface temperatures and increased wind shear.
| Date | Location | Maximum Sustained Winds (mph) | Minimum Central Pressure (mb) |
|---|---|---|---|
| September 8 | Eastern Atlantic | 70 | 1003 |
| September 10 | Central Atlantic | 75 | 988 |
| September 11 | Western Atlantic | 100 | 974 |
Hurricane Helene’s Path and Impact
Hurricane Helene’s path and potential impact were closely monitored by meteorological agencies and emergency management officials. Here’s an overview of its trajectory and the areas it affected:
Approach to the Caribbean
As Hurricane Helene continued its westward movement, it posed a potential threat to the Lesser Antilles and the Caribbean region. The NHC issued hurricane watches and warnings for various islands, including Barbados, St. Lucia, and Martinique. However, as the hurricane neared the region, it began to weaken due to the slightly less favorable conditions it encountered.
By September 12, Helene's maximum sustained winds had decreased to 90 mph (150 km/h), and it was no longer considered a major hurricane (Category 3 or higher). Despite the weakening, the storm still brought heavy rainfall and strong winds to parts of the Lesser Antilles, causing localized flooding and minor damage.
Turn Toward the Open Ocean
Fortunately, Hurricane Helene did not make a direct landfall in the Caribbean. Instead, it began to turn toward the north and northwest, taking a more open-ocean path. This change in trajectory was influenced by a strong high-pressure system located to the north of the hurricane.
As Helene moved away from the Caribbean, it continued to weaken further. By September 15, its maximum sustained winds had decreased to 70 mph (110 km/h), and it was reclassified as a tropical storm. The storm maintained this intensity as it continued its northward journey, remaining well away from any landmasses.
Dissipation and Aftermath
On September 17, Hurricane Helene finally dissipated as it encountered increasingly hostile environmental conditions. The storm’s remnants continued to move northward, eventually merging with a frontal system over the northern Atlantic.
Despite not making a direct landfall, Hurricane Helene's impact was still felt across the Caribbean. The storm's heavy rainfall and strong winds caused localized flooding, especially in low-lying areas and near rivers. Additionally, the storm surge and large waves generated by Helene led to coastal flooding and erosion in some regions.
In the aftermath of the hurricane, emergency response teams and local authorities worked to assess the damage and provide assistance to affected communities. The impact of Helene served as a reminder of the importance of preparedness and the need for robust emergency response plans in vulnerable coastal regions.
Hurricane Helene’s Structural Analysis

Hurricane Helene’s structure and organization played a crucial role in its development and intensity. Here’s a closer look at some key aspects of its structural analysis:
Warm Core Structure
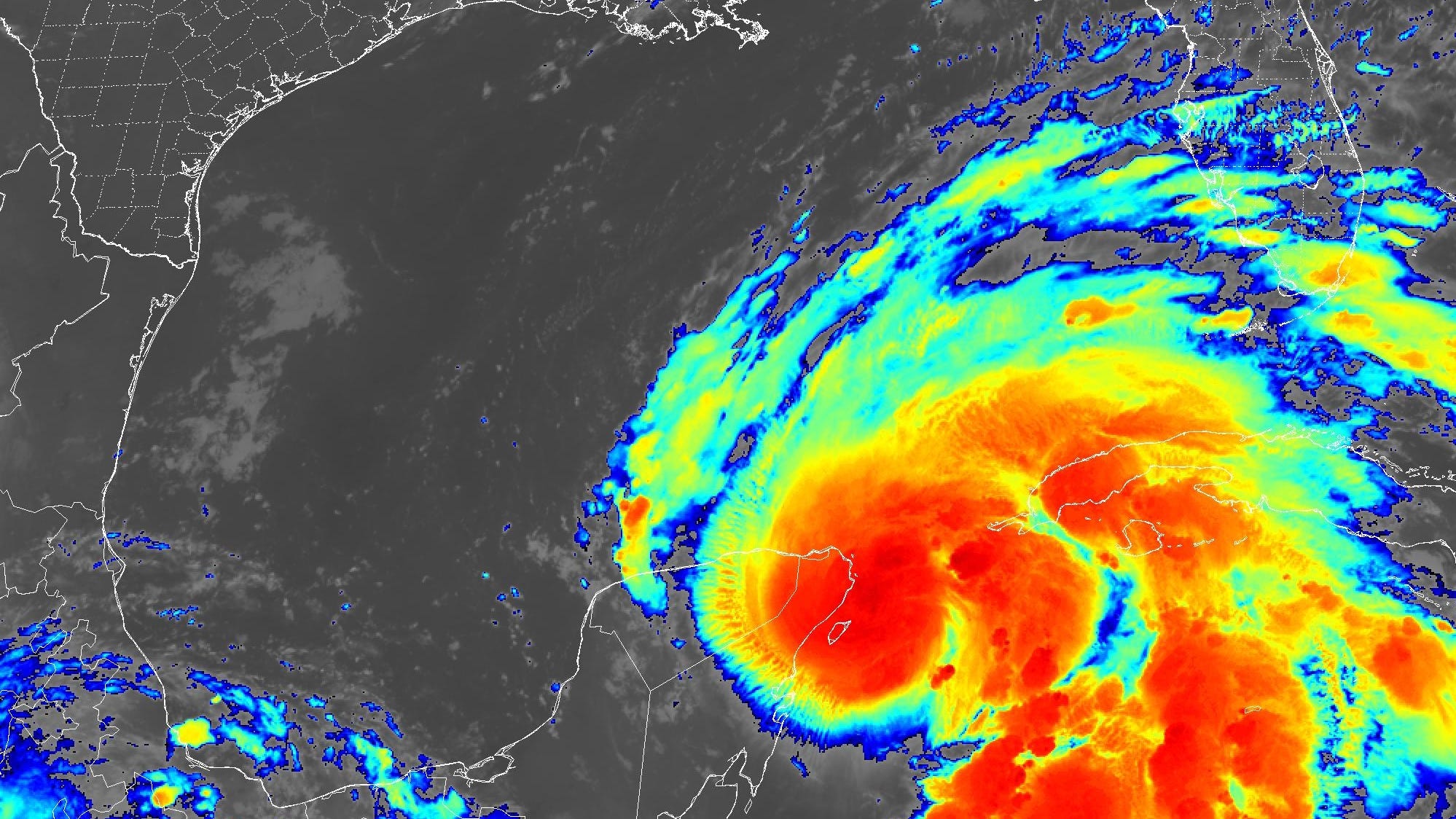
Like all tropical cyclones, Hurricane Helene possessed a warm core structure. This means that the center of the storm, known as the eye, was characterized by warm temperatures and low atmospheric pressure. The warm core structure is a result of the intense convection and heat release within the hurricane’s core, which drives its development and intensification.
The warm core structure of Helene was particularly well-defined, with a clear and distinct eye visible in satellite imagery. This indicated a well-organized and powerful storm system. The warm core also contributed to the hurricane's ability to maintain its intensity over an extended period.
Eyewall and Rainbands
The eyewall of Hurricane Helene was composed of intense thunderstorms and heavy rainfall. The eyewall is the region surrounding the eye of the hurricane, where the most intense winds and rainfall occur. In Helene’s case, the eyewall was relatively compact and well-defined, indicating a strong and organized storm.
Additionally, Helene featured multiple rainbands, which are curved bands of thunderstorms that spiral outward from the hurricane's center. These rainbands can extend for hundreds of miles and are responsible for the heavy rainfall and strong winds associated with hurricanes. In Helene's case, the rainbands were particularly well-defined and contributed to the storm's overall intensity.
Eye Structure and Size
Hurricane Helene’s eye was relatively small, measuring approximately 20 miles (32 km) in diameter at its peak. A smaller eye size is often associated with more intense hurricanes, as it indicates a more concentrated and powerful storm system. The eye’s structure was well-defined, with a clear and distinct circular shape.
The size and structure of the eye can provide valuable insights into a hurricane's intensity and potential for rapid intensification. In the case of Hurricane Helene, the small eye size contributed to its ability to maintain its strength as it moved across the Atlantic.
Hurricane Helene’s Preparedness and Response

Hurricane Helene’s potential impact on coastal regions required a well-coordinated preparedness and response effort. Here’s an overview of the key measures taken to ensure the safety and well-being of vulnerable communities:
Emergency Management and Coordination
In the face of Hurricane Helene’s threat, emergency management agencies and local authorities worked closely together to coordinate response efforts. This included the activation of emergency operations centers, where officials could monitor the storm’s progress, assess potential impacts, and make critical decisions regarding evacuation orders and resource allocation.
Communication played a vital role in the preparedness and response process. Emergency management agencies utilized various channels, including television, radio, and social media, to disseminate timely and accurate information to the public. This included updates on the hurricane's track, potential impacts, and evacuation orders.
Evacuation Plans and Shelters
In areas at risk of direct impact from Hurricane Helene, evacuation plans were put into action. Local authorities identified vulnerable areas, such as low-lying coastal regions and flood-prone areas, and issued evacuation orders to ensure the safety of residents. Evacuation centers and shelters were established to provide temporary housing and support for those who needed to leave their homes.
Evacuation plans and shelters played a crucial role in minimizing the loss of life and reducing the overall impact of the hurricane. By providing a safe and secure environment for those affected, emergency management agencies were able to effectively manage the challenges posed by Hurricane Helene.
Community Engagement and Education
In addition to emergency management efforts, community engagement and education played a significant role in preparing for Hurricane Helene. Local authorities and organizations conducted outreach programs to raise awareness about hurricane preparedness and response. This included distributing informational materials, holding community meetings, and providing training on emergency response procedures.
By empowering communities with knowledge and resources, emergency management agencies aimed to enhance overall resilience and reduce the potential impact of hurricanes. Community engagement also fostered a sense of collective responsibility and cooperation, ensuring that residents were actively involved in their own safety and well-being.
What factors influenced Hurricane Helene's track and intensity?
+Hurricane Helene's track and intensity were influenced by a combination of factors, including the warm sea surface temperatures, low wind shear, and the presence of a strong high-pressure system to the north. These conditions allowed the storm to intensify and maintain its strength as it moved across the Atlantic.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How did Hurricane Helene impact the Caribbean region?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>While Hurricane Helene did not make a direct landfall in the Caribbean, it still brought heavy rainfall and strong winds to parts of the Lesser Antilles. Localized flooding and minor damage were reported in some areas, particularly in low-lying regions and near rivers. The storm surge and large waves generated by Helene also led to coastal flooding and erosion.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What measures were taken to ensure the safety of vulnerable communities during Hurricane Helene?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>To ensure the safety of vulnerable communities, emergency management agencies implemented a range of measures. This included the activation of emergency operations centers, the issuance of evacuation orders in at-risk areas, the establishment of evacuation centers and shelters, and the distribution of timely and accurate information to the public through various communication channels.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>


