Federal Housing Authority Wiki

The Federal Housing Authority (FHA), an integral part of the United States government's housing finance landscape, has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation's housing market and homeownership opportunities since its inception. This authoritative body, with its deep-rooted history and extensive influence, warrants a comprehensive exploration.
The Evolution of the Federal Housing Authority
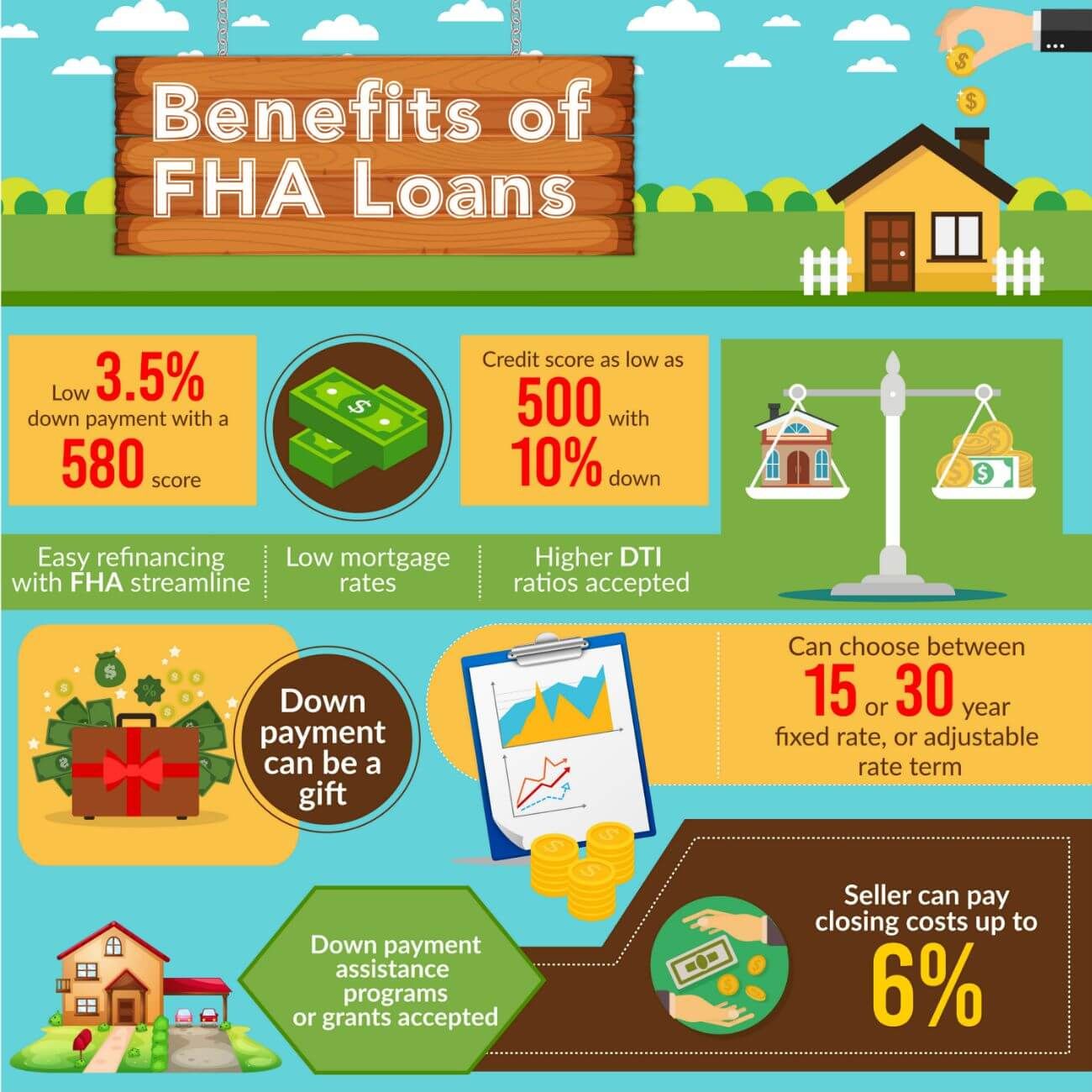
The Federal Housing Authority emerged as a response to the dire housing situation that plagued the United States during the Great Depression. Established in 1934 under the National Housing Act, the FHA was tasked with revitalizing the housing market and making homeownership more accessible to the American populace.
The early years of the FHA were marked by its primary focus on stabilizing the housing market. It achieved this by providing insurance for mortgage loans, thereby encouraging lenders to extend credit to a broader spectrum of borrowers, including those with lower incomes and less substantial down payments. This innovative approach significantly bolstered homeownership rates, especially among first-time buyers and minorities, who had previously faced significant barriers to entry.
Key Milestones in the FHA’s Journey
The FHA’s journey is replete with significant milestones that have shaped its trajectory and impact on the housing market.
- 1938: The FHA expanded its role by introducing the Federal Housing Administration Mortgage Insurance Program. This program, which remains a cornerstone of the FHA's operations today, offered insurance to private lenders against losses incurred on mortgages for home construction or purchase.
- 1965: The FHA underwent a structural change with the establishment of the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). This move solidified the FHA's position as a key component of the federal government's housing policy.
- 1968: The FHA faced a significant challenge with the introduction of the Housing and Urban Development Act. This act, while aimed at enhancing the FHA's role in affordable housing, also brought about substantial changes to its loan programs, leading to a decline in its market share.
- 1974: The FHA implemented the Emergency Home Finance Act, which aimed to address the rising default rates and subsequent financial losses the agency was facing. This act introduced stricter eligibility criteria and loan limits, which, while effective in the short term, led to a reduction in the FHA's market share.
- 1980s: The FHA experienced a resurgence, particularly in the latter half of the decade, as it introduced new loan programs and streamlined its underwriting process. These initiatives, coupled with a robust economy, resulted in a significant increase in the FHA's market share and its impact on the housing market.
The FHA’s Role in the Housing Market

The Federal Housing Authority’s influence on the housing market is profound and multifaceted. By providing mortgage insurance, the FHA has incentivized lenders to offer loans to borrowers who might otherwise be considered high-risk. This has had a direct impact on homeownership rates, particularly among those with lower incomes and those who are first-time buyers.
FHA Loan Programs
The FHA offers a range of loan programs designed to cater to different borrower needs and circumstances. These programs include:
- FHA 203(b) Loan Program: This is the most common FHA loan program, designed for individuals purchasing a primary residence. It offers low down payment requirements and flexible credit score criteria.
- FHA 203(k) Rehabilitation Loan Program: Aimed at homebuyers interested in purchasing and rehabilitating a home, this program provides funds for both the purchase and renovation of the property.
- FHA Energy-Efficient Mortgage (EEM) Program: This program assists borrowers in purchasing energy-efficient homes or making energy-efficient improvements to their existing homes.
- FHA Back to Work Program: Introduced in 2013, this program provides a second chance for borrowers who experienced financial hardship due to unemployment or a significant income reduction.
| Loan Program | Key Features |
|---|---|
| FHA 203(b) | Low down payment, flexible credit score criteria |
| FHA 203(k) | Caters to home renovation needs |
| FHA EEM | Encourages energy-efficient home purchases and improvements |
| FHA Back to Work | Offers a second chance to borrowers who have experienced financial hardship |

Impact on Homeownership
The FHA’s mortgage insurance programs have been instrumental in expanding homeownership opportunities. By insuring loans for borrowers who might not meet the stringent criteria of conventional loans, the FHA has enabled millions of Americans to achieve the dream of homeownership. This has had a profound impact on the nation’s social fabric, contributing to the development of stable communities and fostering a sense of belonging and investment in local areas.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its significant contributions, the FHA has not been without its share of challenges and criticisms. One of the primary concerns has been the agency’s financial stability. Over the years, the FHA has faced periods of financial strain, particularly during economic downturns when default rates rise. This has led to calls for reforms and a reevaluation of its loan programs and underwriting standards.
Financial Stability Concerns
The FHA’s financial stability has been a recurring issue, with the agency facing significant financial losses during periods of economic downturn. In response, the FHA has implemented various measures, including raising insurance premiums and tightening loan requirements, to bolster its financial position. However, these measures have often been met with criticism, as they can limit access to credit for borrowers who rely on FHA loans.
Loan Program Criticisms
The FHA’s loan programs have also been the subject of criticism. Some critics argue that certain programs, particularly those with more flexible criteria, have contributed to a culture of risky lending and have the potential to lead to another housing market collapse. Additionally, there have been concerns about the FHA’s impact on the overall housing market, with some arguing that its presence distorts market forces and hinders the development of a healthy, sustainable housing market.
The Future of the FHA

Looking ahead, the Federal Housing Authority is poised to continue its vital role in the U.S. housing market. With a focus on accessibility and financial stability, the FHA will likely continue to adapt its loan programs and underwriting standards to meet the evolving needs of borrowers and the changing economic landscape.
Proposed Reforms and Initiatives
The FHA is actively engaged in proposing and implementing reforms to enhance its operations and address its financial stability concerns. These reforms include:
- Implementing risk-based pricing for mortgage insurance premiums, which would adjust premiums based on the risk profile of the borrower.
- Expanding its loan limits to cater to a broader range of borrowers, particularly in high-cost areas.
- Introducing new loan programs and improving existing ones to better meet the needs of underserved populations, such as first-time homebuyers and minority communities.
The Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are also expected to play a significant role in the FHA’s future. The agency is exploring ways to leverage technology to streamline its processes, enhance its data analytics capabilities, and improve the overall borrower experience. This includes the potential adoption of digital mortgage applications and the use of artificial intelligence for more efficient loan underwriting.
What is the primary role of the Federal Housing Authority?
+The primary role of the Federal Housing Authority is to stabilize and expand the U.S. housing market by providing mortgage insurance for loans made by FHA-approved lenders. This insurance encourages lenders to extend credit to a broader spectrum of borrowers, including those with lower incomes and less substantial down payments.
How has the FHA impacted homeownership rates in the U.S.?
+The FHA has had a significant impact on homeownership rates, particularly among first-time buyers and minorities. By providing mortgage insurance for loans with lower down payment requirements and more flexible credit criteria, the FHA has made homeownership more accessible to these populations, contributing to the development of stable communities and fostering a sense of belonging and investment in local areas.
What are some of the challenges faced by the FHA?
+The FHA has faced challenges related to its financial stability, particularly during economic downturns when default rates rise. There have also been criticisms of its loan programs, with concerns raised about the potential for risky lending and the impact of its presence on the overall housing market.


