Corn Nutrition: Unlocking The Power Of Whole Grains

Corn, a staple crop with a rich history, is a powerhouse of nutrition. Beyond its use in traditional cuisines, corn offers a myriad of health benefits and versatile applications. From its high fiber content to its essential vitamins and minerals, corn plays a crucial role in a balanced diet. This article delves into the nutritional profile of corn, exploring its benefits, applications, and the science behind its power as a whole grain.
The Nutritional Profile of Corn

Corn, scientifically known as Zea mays, is a cereal grain that belongs to the grass family. It is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a unique combination of essential nutrients that contribute to overall health and well-being. Here’s a closer look at the key components of corn’s nutritional profile:
Macronutrients
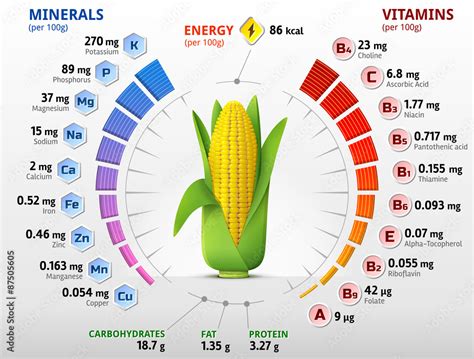
Corn is primarily composed of carbohydrates, with a significant proportion being complex carbohydrates. These complex carbs provide a steady source of energy, promoting sustained energy levels throughout the day. Additionally, corn contains a moderate amount of protein, which is essential for muscle repair and growth. While corn is not a complete protein source, it can be combined with other plant-based proteins to ensure an adequate intake of all essential amino acids.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 28.2g |
| Protein | 3.3g |
| Fat | 1.4g |

Fiber
One of the standout nutritional benefits of corn is its high fiber content. Fiber is essential for digestive health, helping to regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. Additionally, fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is linked to overall well-being. The fiber in corn is primarily in the form of insoluble fiber, which adds bulk to the diet and promotes a feeling of fullness, making it a valuable tool for weight management.
Vitamins and Minerals
Corn is a rich source of several essential vitamins and minerals. It is particularly high in vitamin B6, which is crucial for brain development and function. Additionally, corn contains significant amounts of folate, which is essential for cell growth and division, making it especially important during pregnancy. Corn is also a good source of minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for various bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, bone health, and fluid balance.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.1mg |
| Folate | 38μg |
| Magnesium | 37mg |
| Phosphorus | 91mg |
| Potassium | 280mg |
Antioxidants
Corn is a rich source of antioxidants, which are compounds that help protect the body against the harmful effects of free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases. The antioxidants in corn, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, are particularly beneficial for eye health, as they help protect the eyes from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Health Benefits of Corn
The nutritional profile of corn offers a range of health benefits. Here are some key advantages of incorporating corn into your diet:
Digestive Health
As mentioned earlier, the high fiber content in corn promotes digestive health. Fiber adds bulk to the diet, aiding in the smooth passage of food through the digestive tract. This can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. Additionally, fiber plays a role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is linked to overall digestive health and immune function.
Heart Health
The fiber and antioxidants in corn contribute to heart health. The insoluble fiber in corn helps lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the antioxidants in corn, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, have been shown to have a protective effect on the heart, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Weight Management
Corn can be a valuable tool for weight management due to its high fiber content. Fiber adds bulk to the diet, promoting a feeling of fullness and satiety. This can help control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, the complex carbohydrates in corn provide a steady release of energy, preventing energy crashes and cravings that can lead to unhealthy snacking.
Eye Health
The antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin found in corn are particularly beneficial for eye health. These antioxidants help protect the eyes from the harmful effects of blue light and UV radiation, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Including corn in your diet can contribute to maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of eye-related diseases.
Versatility of Corn

Corn is not only nutritious but also incredibly versatile. It can be enjoyed in various forms and incorporated into a wide range of dishes. Here are some popular ways to enjoy corn:
Whole Kernel Corn
Whole kernel corn, also known as sweet corn, is a popular choice for grilling, boiling, or roasting. It can be enjoyed as a side dish, added to salads, or used as a topping for dishes like tacos or pizzas. Sweet corn is particularly delicious when it’s in season and freshly picked.
Cornmeal
Cornmeal is a finely ground form of corn that is used in a variety of dishes. It is a key ingredient in cornbread, a staple in many cuisines. Cornmeal can also be used to make polenta, a versatile dish that can be served as a side or a main course. Additionally, cornmeal is commonly used as a coating for fried foods, adding a crispy texture and a unique flavor.
Corn Flour
Corn flour, also known as cornstarch, is a fine powder made from corn. It is commonly used as a thickening agent in sauces, soups, and gravies. Corn flour can also be used in baking, adding a unique texture and flavor to cakes, cookies, and other baked goods. It is a popular ingredient in gluten-free baking, as it provides structure and texture without the use of gluten.
Corn Tortillas
Corn tortillas are a staple in Mexican cuisine. They are made from masa harina, a type of corn flour, and water. Corn tortillas can be used as a base for tacos, enchiladas, and burritos, or enjoyed as a snack with a variety of fillings and toppings. They are a versatile and healthy alternative to wheat tortillas, offering a unique flavor and texture.
Conclusion

Corn is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a unique combination of essential nutrients and health benefits. From its high fiber content to its rich array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, corn plays a crucial role in a balanced diet. Whether enjoyed as whole kernel corn, cornmeal, corn flour, or corn tortillas, corn adds flavor, texture, and nutritional value to a wide range of dishes. Incorporating corn into your diet can contribute to overall health and well-being, making it a valuable addition to any meal plan.
Is corn gluten-free?
+Yes, corn is naturally gluten-free. However, it is important to be cautious when consuming processed corn products, as they may be contaminated with gluten during manufacturing. Look for certified gluten-free products to ensure a safe and gluten-free option.
Can corn be part of a low-carb diet?
+While corn is primarily a carbohydrate, it can still be included in a low-carb diet in moderation. The key is to be mindful of portion sizes and to balance the intake of corn with other low-carb foods. Consult with a registered dietitian to create a personalized low-carb meal plan that includes corn.
Is corn a good source of protein?
+Corn contains a moderate amount of protein, but it is not a complete protein source. To ensure an adequate intake of all essential amino acids, it is recommended to combine corn with other plant-based proteins, such as beans, nuts, or seeds.


