Black And White Bee

The Black and White Bee, scientifically known as Panurgus calcaratus, is a fascinating species of bee that stands out due to its distinctive coloration and unique characteristics. Unlike the more commonly known honey bees or bumblebees, the Black and White Bee has a more solitary lifestyle and exhibits some intriguing behaviors and adaptations. This species is native to Europe and can be found in various habitats, from meadows and grasslands to forest edges. Its ecological role and behavior make it an important and intriguing subject of study for entomologists and ecologists alike.
Physical Characteristics and Behavior
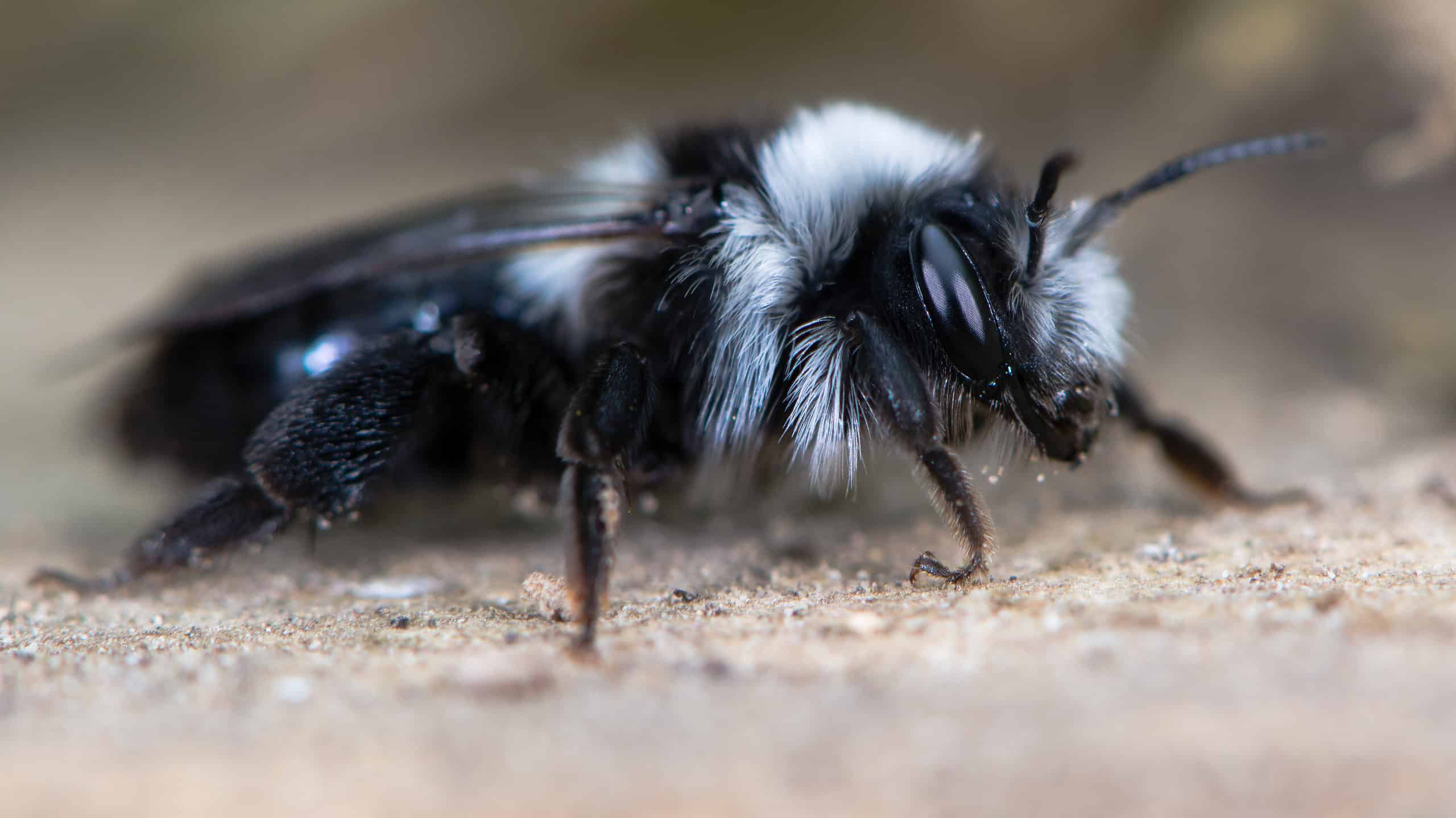

The Black and White Bee is a medium-sized bee, typically measuring around 12-15 mm in length. Its most striking feature is its contrasting black and white coloration, which serves as a form of aposematic (warning) coloration, warning potential predators of its ability to deliver a painful sting. The body of the bee is covered in a layer of fine, dense hairs, which, along with its coloration, helps it blend into its surroundings, providing camouflage against potential threats.
Despite its solitary nature, the Black and White Bee is not entirely antisocial. During the mating season, large numbers of males can be seen congregating in leks, where they display and compete for the attention of females. These lekking behaviors are relatively rare among bees and provide an intriguing insight into the social dynamics of this species.
Nest Building and Reproduction
Female Black and White Bees are known for their meticulous nest-building skills. They construct their nests in the ground, often in areas with well-drained soil and good access to floral resources. Each female creates a series of cells within the nest, each containing a single egg and a supply of pollen and nectar to nourish the developing larvae. This maternal care and investment in offspring are relatively uncommon among solitary bee species and highlight the unique reproductive strategies of Panurgus calcaratus.
After the eggs hatch, the larvae feed on the provisioned pollen and nectar, eventually spinning a cocoon and pupating. The adult bees emerge the following spring, ready to start the cycle anew. This annual life cycle is typical of many bee species and ensures the continuation of the population.
Ecology and Floral Interactions

The Black and White Bee plays a crucial role in the ecosystems it inhabits, acting as an important pollinator for a variety of plant species. Its preference for certain types of flowers and its efficient pollination techniques contribute to the reproductive success of many plant species, thus maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Black and White Bee's ecology is its specialized relationship with certain plant species. For example, it has been observed to have a strong preference for flowers in the Apiaceae family, such as wild carrot and cow parsley. This mutualistic relationship, where the bee benefits from the nectar and the plant benefits from pollination, is a prime example of the intricate web of interactions that sustain ecosystems.
Conservation and Threats
Like many bee species, the Black and White Bee faces various threats that could impact its population and ecological role. Habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities, such as urbanization and intensive agriculture, are significant concerns. Pesticide use can also have detrimental effects on bee populations, as can the introduction of non-native bee species that may compete for resources.
Conservation efforts for the Black and White Bee and other bee species often focus on preserving and restoring their natural habitats, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and raising awareness about the importance of pollinators in our ecosystems. Protecting these bees is not just about preserving a single species but about safeguarding the intricate web of life that depends on their ecological services.
Research and Future Directions
The study of the Black and White Bee offers numerous avenues for further research and discovery. For instance, investigating the specific mechanisms and chemicals involved in its aposematic coloration could provide insights into the evolution of warning signals in nature. Additionally, exploring the unique lekking behaviors of this species could offer new perspectives on social dynamics and mating strategies among solitary bees.
Furthermore, given the critical role of bees in pollination and their declining populations worldwide, studying the Black and White Bee's ecological interactions and its resilience to various environmental stressors could inform conservation strategies and help ensure the continued survival of this and other bee species. As our understanding of these fascinating creatures deepens, so too does our appreciation for the intricate balance of nature and the importance of conserving our biodiversity.
What makes the Black and White Bee unique among other bee species?
+The Black and White Bee stands out for its contrasting black and white coloration, which serves as a warning signal to potential predators. Additionally, its solitary nature, intricate nest-building skills, and specialized relationship with certain plant species set it apart from more social bee species like honey bees or bumblebees.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What is the ecological significance of the Black and White Bee's aposematic coloration?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The bee's aposematic coloration acts as a warning signal, indicating to potential predators that it is capable of delivering a painful sting. This helps deter predators and reduce the risk of attack, ensuring the bee's survival and allowing it to continue its important role as a pollinator.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does the Black and White Bee contribute to plant reproduction?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>As a pollinator, the Black and White Bee plays a crucial role in the reproductive success of many plant species. When the bee visits flowers to collect nectar and pollen, it inadvertently transfers pollen from one flower to another, facilitating fertilization and the production of seeds. This mutualistic relationship ensures the continuation of plant species and contributes to the overall health and diversity of ecosystems.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>