Bison Meat Vs Beef: A Comprehensive Taste And Health Comparison
When it comes to meat, two popular options that often come to mind are bison and beef. Both meats have their unique characteristics, flavors, and nutritional profiles. In this comprehensive comparison, we delve into the taste, health benefits, and differences between bison meat and beef, exploring why each choice might be preferred by different consumers.
Taste Profile: Bison Meat vs. Beef
The taste of meat is a highly subjective experience, influenced by personal preferences and cultural backgrounds. However, there are distinct differences in the flavor profiles of bison and beef that are worth exploring.
Bison Meat: A Leaner, Earthier Delight
Bison meat, also known as buffalo meat, is renowned for its lean and robust flavor. It has a slightly sweeter and more delicate taste compared to beef, often described as having a hint of gamey character. This unique flavor profile is attributed to the bison’s natural diet of grasses and forbs, which contributes to a leaner and more nutritious meat.
The leanness of bison meat means it tends to be slightly drier than beef, which can be a preference for those who enjoy a more robust and distinct flavor. However, this can also be mitigated by proper cooking techniques and the addition of moist ingredients or marinades.
Beef: A Classic, Rich Flavor
Beef, a staple in many cuisines worldwide, is characterized by its rich, savory taste. It has a more intense and robust flavor compared to bison, with a higher fat content contributing to a juicier and more tender texture. The marbling of fat in beef is often associated with a richer, more indulgent eating experience.
Beef's flavor can vary depending on the cut and the animal's diet and living conditions. Grass-fed beef, for instance, may have a slightly different taste profile compared to grain-fed beef, with a more nuanced and complex flavor.
Texture and Mouthfeel
In terms of texture, bison meat tends to be slightly firmer and more fibrous than beef. This is due to the bison’s leaner composition and the fact that bison meat has less intramuscular fat, resulting in a meat that is denser and chewier. On the other hand, beef, with its higher fat content, tends to be more tender and melt-in-your-mouth, especially when cooked to the right temperature.
The texture differences between bison and beef can be a matter of personal preference. Some people appreciate the robust, chewy texture of bison, while others prefer the tender, juicy mouthfeel of beef.
Nutritional Value: Bison Meat vs. Beef
Both bison and beef are excellent sources of high-quality protein and essential nutrients. However, there are some notable differences in their nutritional profiles that can impact your choice, especially if you have specific dietary goals or health concerns.
Protein and Fat Content
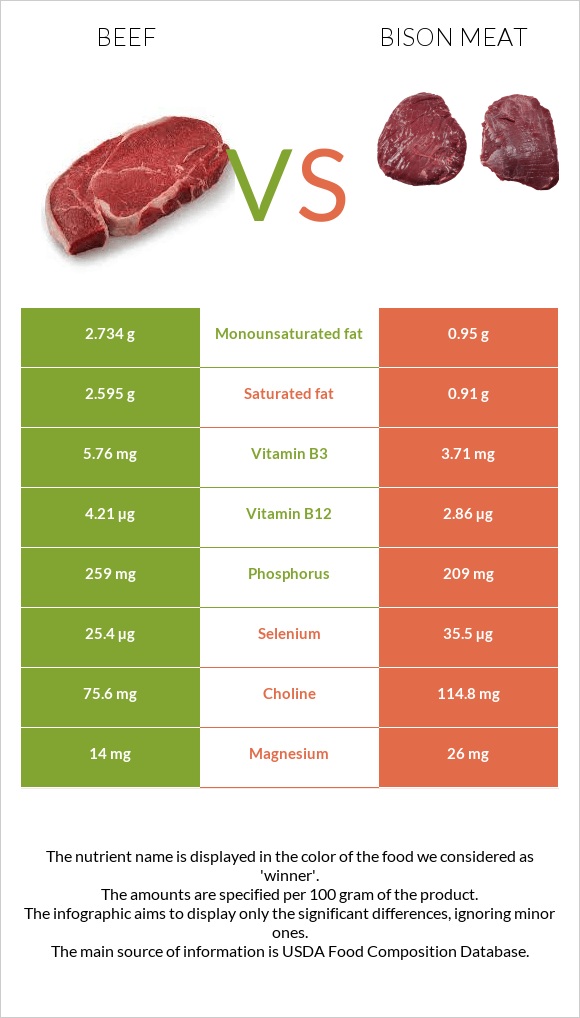
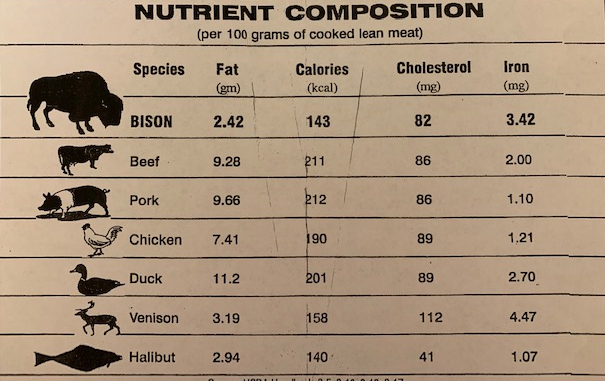
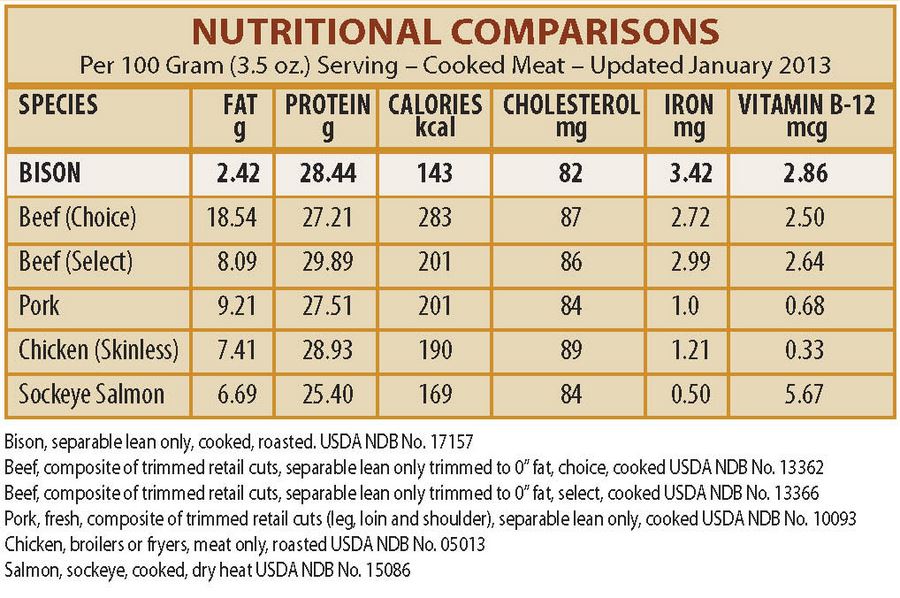
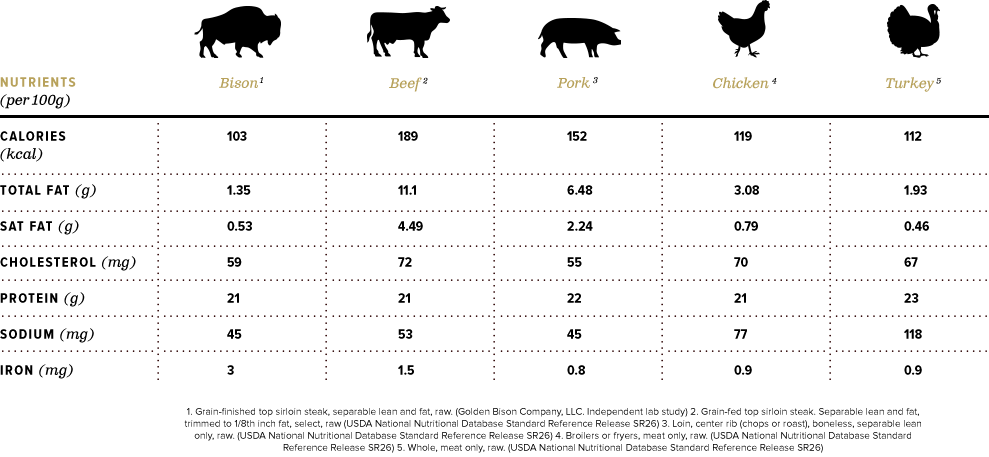
Bison meat is an excellent source of lean protein, containing fewer calories and less fat than beef. A 3-ounce serving of cooked bison meat typically provides around 18 grams of protein and only 100-120 calories, with less than 3 grams of fat. This makes bison meat an attractive option for those watching their calorie and fat intake, or those following a low-fat diet.
In contrast, beef is also an excellent source of protein but tends to have a higher fat content. A 3-ounce serving of cooked beef can provide around 20-25 grams of protein but can range from 150-200 calories, with 7-12 grams of fat. The fat content in beef can vary significantly depending on the cut and the animal's diet.
Vitamin and Mineral Content
Both bison and beef are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Bison meat is particularly high in iron, with a 3-ounce serving providing around 2-3 milligrams of iron, which is about 10-15% of the recommended daily intake for adults. It is also a good source of B vitamins, including niacin, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12.
Beef is also an excellent source of iron, with similar levels to bison, and is rich in B vitamins, particularly vitamin B12. Additionally, beef is a good source of zinc, with a 3-ounce serving providing around 5-7 milligrams, which is approximately 30-40% of the recommended daily intake for adults.
| Nutrient | Bison Meat | Beef |
|---|---|---|
| Protein (per 3 oz) | 18 g | 20-25 g |
| Calories (per 3 oz) | 100-120 | 150-200 |
| Fat (per 3 oz) | 2-3 g | 7-12 g |
| Iron (per 3 oz) | 2-3 mg | 2-3 mg |
| Vitamin B12 (per 3 oz) | 3-4 mcg | 2-3 mcg |
| Zinc (per 3 oz) | 3-4 mg | 5-7 mg |
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
One notable difference between bison and beef is their omega-3 fatty acid content. Bison meat is a richer source of omega-3 fatty acids compared to beef, particularly when the bison are grass-fed. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for heart health and brain function, and their presence in bison meat makes it an attractive choice for those looking to increase their omega-3 intake.
Saturated Fat and Cholesterol
Beef, especially cuts with higher fat content, tends to have more saturated fat and cholesterol compared to bison. While saturated fat and cholesterol are not inherently bad for you, they should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Bison meat, with its lower fat content, can be a preferred choice for those concerned about their saturated fat and cholesterol intake.
Culinary Versatility and Cooking Methods

Both bison and beef are highly versatile in the kitchen and can be prepared in a variety of ways. The choice of cooking method can significantly impact the taste and texture of the meat, and the right technique can enhance the natural flavors of each.
Bison Meat: Lean and Quick Cooking
Bison meat, due to its lean nature, benefits from quick cooking methods that preserve its juiciness and prevent it from becoming tough. Grilling, pan-searing, and roasting are popular choices for bison, as these methods cook the meat quickly and seal in the juices. Slow-cooking methods, while possible, can result in a drier texture due to the lack of fat.
When cooking bison, it's important to keep an eye on the temperature to avoid overcooking. Bison meat is best served at medium-rare to medium doneness, which helps maintain its moisture and flavor. Marinades and rubs can also be used to enhance the flavor and add a touch of moisture to the lean meat.
Beef: Versatile and For All Occasions
Beef, with its higher fat content, is more forgiving when it comes to cooking methods. It can be prepared using a variety of techniques, from slow-cooking to quick searing, depending on the cut and desired outcome. Stewing, braising, grilling, and roasting are all popular ways to prepare beef, each bringing out different flavors and textures.
For tougher cuts of beef, such as brisket or chuck roast, slow-cooking methods are ideal to break down the connective tissues and create a tender, flavorful dish. On the other hand, for leaner cuts like sirloin or tenderloin, quick cooking methods like grilling or pan-searing can preserve the meat's tenderness and juiciness.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
In addition to taste and nutritional value, the choice between bison and beef can also be influenced by environmental and ethical concerns. The impact of meat production on the environment and animal welfare is an important consideration for many consumers.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bison, being a native North American species, is often considered more environmentally friendly than beef. Bison are well-adapted to the North American climate and require less resources, such as water and grain, compared to beef cattle. Additionally, bison grazing can help promote biodiversity and maintain the health of grasslands, making it a more sustainable choice.
Beef production, on the other hand, can have a larger environmental footprint due to the resources required for feed production, water usage, and the emissions associated with cattle farming. However, it's important to note that the environmental impact of beef production can vary greatly depending on the farming practices and the region.
Animal Welfare and Ethical Farming
When it comes to animal welfare, both bison and beef farming can vary greatly depending on the specific farm and the practices employed. Some farmers prioritize animal welfare and use humane practices, while others may focus more on efficiency and profitability.
Bison, being a wild animal that has been domesticated, often have more space to roam and graze freely compared to beef cattle. This can result in a more natural and stress-free life for the bison. However, it's important to research and choose bison meat from farms that prioritize animal welfare and sustainable practices.
For beef, there has been a growing movement towards more ethical and sustainable farming practices, such as grass-fed and pasture-raised beef. These practices often involve allowing cattle to graze on natural pastures, which can improve their welfare and the quality of the meat. Again, it's important to research and support farms that align with your values.
Conclusion: The Right Choice for You

The choice between bison meat and beef ultimately depends on personal preferences, dietary needs, and ethical considerations. Both meats have their unique flavors, nutritional profiles, and culinary uses that can cater to different tastes and lifestyles.
Bison meat, with its leaner composition, sweeter flavor, and higher omega-3 content, can be an excellent choice for those looking for a healthier, more sustainable option. It is particularly appealing to those who are health-conscious, environmentally aware, or follow a low-fat diet.
Beef, on the other hand, offers a richer, more indulgent flavor and a higher fat content, making it a favorite for those who enjoy a more traditional, juicy meat experience. It is versatile and can be prepared in a variety of ways to suit different tastes and occasions.
Ultimately, the best choice is the one that aligns with your personal preferences, dietary needs, and values. Whether you choose bison or beef, both meats can be delicious and nutritious additions to your diet when prepared and sourced responsibly.
Can bison meat be used as a substitute for beef in recipes?
+Yes, bison meat can be used as a substitute for beef in many recipes. However, due to its leaner nature, it may require some adjustments in cooking time and method. Bison cooks faster than beef, so it’s important to monitor the temperature closely to avoid overcooking. Additionally, adding a bit of moisture, such as a marinade or cooking liquid, can help prevent the meat from becoming dry.
Is bison meat more expensive than beef?
+In general, bison meat tends to be more expensive than beef. This is due to a combination of factors, including the smaller population of bison compared to cattle, the specialized farming and processing required, and the growing demand for bison meat as a healthier and more sustainable option. However, the price can vary depending on the cut, the region, and the specific supplier.
What are some popular cuts of bison meat and how should they be cooked?
+Some popular cuts of bison meat include the tenderloin, sirloin, ribeye, and ground bison. The tenderloin is a lean and tender cut that is best suited for quick cooking methods like grilling or pan-searing. The sirloin is a slightly tougher cut that benefits from marinating and slow cooking. The ribeye is a flavorful cut that can be grilled or roasted, and ground bison can be used in a variety of dishes like burgers, meatballs, or meatloaf.
Are there any health concerns associated with consuming bison meat or beef?
+Both bison and beef are generally safe to consume as part of a balanced diet. However, as with any meat, it’s important to ensure proper handling and cooking to prevent foodborne illnesses. Additionally, for those with specific dietary restrictions or health conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion sizes and frequency of consumption.


