Army Ant Sutures: A Comprehensive Guide To Effective Wound Closure
Army Ant Sutures, also known as surgical sutures or stitches, are an essential tool in the field of medicine, particularly in wound closure and surgical procedures. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of Army Ant Sutures, their types, applications, and the importance they hold in the medical field. With the ever-evolving nature of medical technology, it is crucial to stay updated on the latest advancements in wound closure techniques, and Army Ant Sutures play a significant role in this domain.
Understanding Army Ant Sutures: An Overview

Army Ant Sutures are medical devices used to approximate and close wounds, incisions, or surgical openings. They are an integral part of the surgical process, aiding in the healing and recovery of patients by promoting tissue adhesion and reducing the risk of infection. These sutures are typically made from a variety of materials, including natural and synthetic fibers, each offering unique benefits and applications.
Types of Army Ant Sutures
Army Ant Sutures come in a wide range of types, each designed for specific purposes and body parts. Here are some of the most common types:
- Absorbable Sutures: These sutures are designed to be broken down and absorbed by the body over time. They are commonly used in internal surgeries or situations where removal might be difficult. Examples include Catgut and Polydioxanone sutures.
- Non-Absorbable Sutures: In contrast, non-absorbable sutures are not broken down by the body and require removal after the wound has healed. They are often used for external wounds and surgeries, such as Nylon and Polypropylene sutures.
- Barbed Sutures: A relatively new innovation, barbed sutures have barbs along their length that allow them to hold tissues together without the need for traditional knot tying. This type of suture is particularly useful in minimally invasive surgeries.
- Tissue-Specific Sutures: Certain sutures are designed for specific tissues or organs, such as Cardiac Sutures for heart surgeries or Ophthalmic Sutures for eye surgeries. These sutures are crafted to meet the unique requirements of these delicate procedures.
Applications of Army Ant Sutures
The applications of Army Ant Sutures are vast and diverse, covering a wide range of medical procedures and specialties. Here are some key areas where sutures are commonly used:
- General Surgery: Sutures are fundamental in general surgical procedures, such as appendectomies, hernia repairs, and gallbladder removals. They aid in closing incisions and preventing infections.
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: In these specialized fields, sutures play a crucial role in achieving precise and aesthetically pleasing results. They are used to close wounds, reduce scarring, and support tissue reconstruction.
- Orthopedic Surgery: Army Ant Sutures are essential for fixing fractures, repairing tendons and ligaments, and performing joint replacements. They provide stability and promote healing in these complex procedures.
- Ophthalmology: Sutures are used in eye surgeries, such as cataract removal or corneal transplants, to ensure precise and delicate tissue closure.
- Gynecological Surgeries: In procedures like hysterectomies or cesarean sections, sutures are used to close incisions and support the healing process.
The Science Behind Army Ant Sutures

The effectiveness of Army Ant Sutures lies in their ability to provide mechanical support to tissues, promote healing, and prevent complications. Here’s a closer look at the science behind their functionality:
Mechanical Properties
Sutures must possess the right mechanical properties to withstand the forces applied to them during and after surgery. These properties include tensile strength, which ensures the suture can withstand the tension applied by the surrounding tissues, and knot security, which prevents the suture from loosening or slipping.
Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility is a critical aspect of sutures, as they must be well-tolerated by the body to avoid adverse reactions. Absorbable sutures, for instance, are designed to be broken down by the body’s natural processes without causing inflammation or toxicity.
Tissue Adhesion
Sutures must adhere to tissues effectively to hold them together during the healing process. This adhesion is influenced by factors such as the suture material, the technique used to place the suture, and the tissue’s own healing response.
Infection Prevention
Sutures play a crucial role in preventing infections by providing a physical barrier against microorganisms. Proper handling, sterilization, and placement techniques are essential to minimize the risk of infection.
| Suture Type | Infection Risk |
|---|---|
| Absorbable Sutures | Lower risk due to their rapid absorption |
| Non-Absorbable Sutures | Higher risk if not removed timely |
Choosing the Right Army Ant Suture

Selecting the appropriate Army Ant Suture for a specific procedure is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind when choosing sutures:
Tissue Type and Location
Different tissues and body parts have unique characteristics and healing properties. For instance, skin sutures require different considerations compared to those used for internal organs. The choice of suture material and technique should be tailored to the specific tissue and its healing requirements.
Healing Time
The estimated healing time for a wound or incision is a crucial factor in suture selection. Absorbable sutures are often preferred for procedures with shorter healing times, while non-absorbable sutures are chosen for longer-term support.
Patient Factors
Patient-specific factors, such as age, overall health, and immune status, can influence the choice of suture. For example, older patients or those with compromised immune systems may benefit from faster-absorbing sutures to reduce the risk of infection.
Surgical Technique
The surgical technique and the surgeon’s preference play a significant role in suture selection. Some surgeons may have a preferred suture type or technique based on their experience and the specific procedure being performed.
Advancements in Army Ant Suture Technology

The field of Army Ant Sutures is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and development leading to significant advancements. Here are some notable innovations:
Smart Sutures
Smart sutures are a revolutionary concept that integrates technology into traditional sutures. These sutures can monitor and transmit real-time data, such as temperature, pH levels, and tissue oxygenation, providing valuable insights into the healing process. This technology enables early detection of complications and facilitates more precise wound management.
Biomimetic Sutures
Biomimetic sutures are designed to mimic the natural structure and function of human tissues. By replicating the properties of native tissues, these sutures promote faster healing and reduce scarring. This approach is particularly beneficial in cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries.
Antimicrobial Sutures
Infection prevention is a critical aspect of wound closure. Antimicrobial sutures are coated with substances that inhibit the growth of bacteria, reducing the risk of infection. These sutures are particularly useful in high-risk procedures or for patients with compromised immune systems.
Future Implications and Research Directions
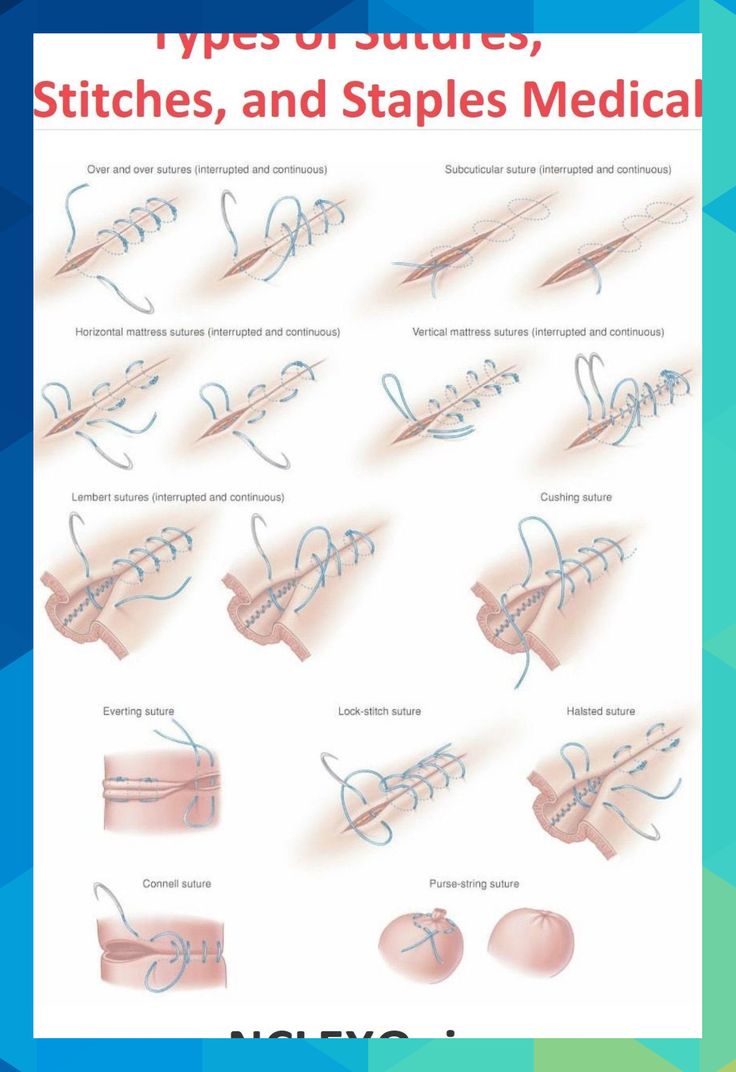
The future of Army Ant Sutures holds promising advancements and research opportunities. Here are some potential directions for further exploration:
Personalized Sutures
With the advent of personalized medicine, the development of customized sutures tailored to individual patient needs is an exciting prospect. This could involve creating sutures with specific mechanical properties, biodegradation rates, or even patient-specific biomaterials.
Minimally Invasive Suturing Techniques
As minimally invasive surgeries continue to gain popularity, the development of specialized suturing techniques and tools for these procedures is essential. This includes the use of robotic-assisted suturing systems and the further refinement of barbed sutures.
Regenerative Medicine and Sutures
Integrating regenerative medicine principles into suture design could lead to innovative solutions for wound healing. This could involve the use of stem cells, growth factors, or other biological materials to enhance tissue regeneration and reduce scarring.
What are the potential complications associated with Army Ant Sutures?
+While Army Ant Sutures are generally safe and effective, complications can occasionally arise. These may include infection, excessive scarring, suture failure, or allergic reactions to the suture material. Proper technique, patient selection, and post-operative care can help minimize these risks.
How long do Army Ant Sutures take to dissolve or absorb?
+The absorption or dissolution time of Army Ant Sutures varies depending on the type of suture and the individual’s healing capacity. Absorbable sutures typically dissolve within a few weeks to several months, while non-absorbable sutures may require removal after the wound has healed, which can take several weeks.
Are there any alternatives to Army Ant Sutures for wound closure?
+Yes, there are alternative methods for wound closure, including skin adhesives, staples, and tissue adhesives. The choice between sutures and these alternatives depends on factors such as wound location, size, depth, and the patient’s overall health.



