Amur River Maple
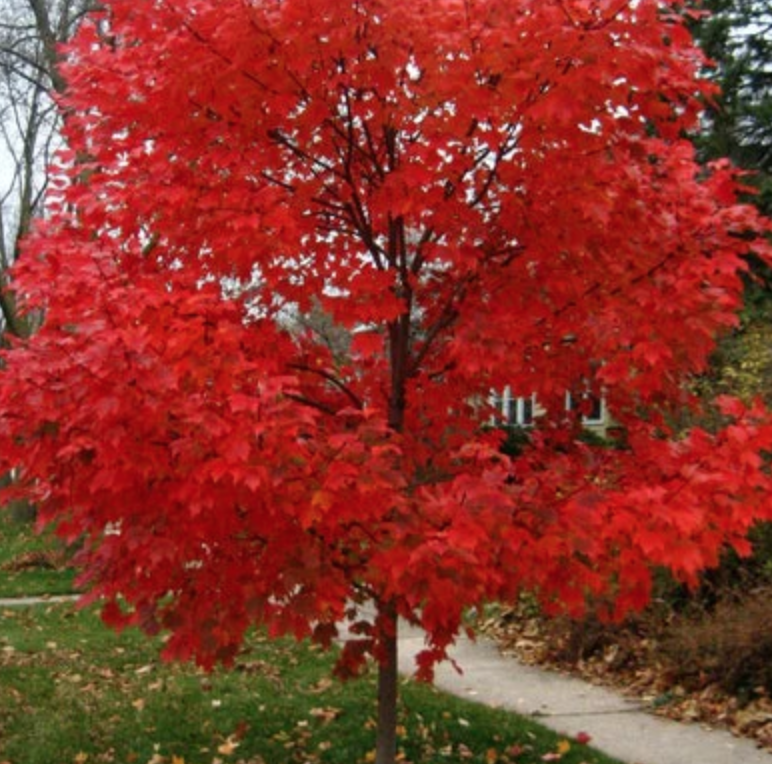

The Amur River Maple, scientifically known as Acer ginnala, is a captivating deciduous tree native to East Asia. With its elegant form and vibrant foliage, this maple species has become a popular choice for landscaping and ornamental purposes, particularly in regions with cold winters. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of the Amur River Maple, exploring its unique characteristics, cultivation requirements, and the significant role it plays in ecosystems and landscapes.
Botanical Overview and Natural Habitat
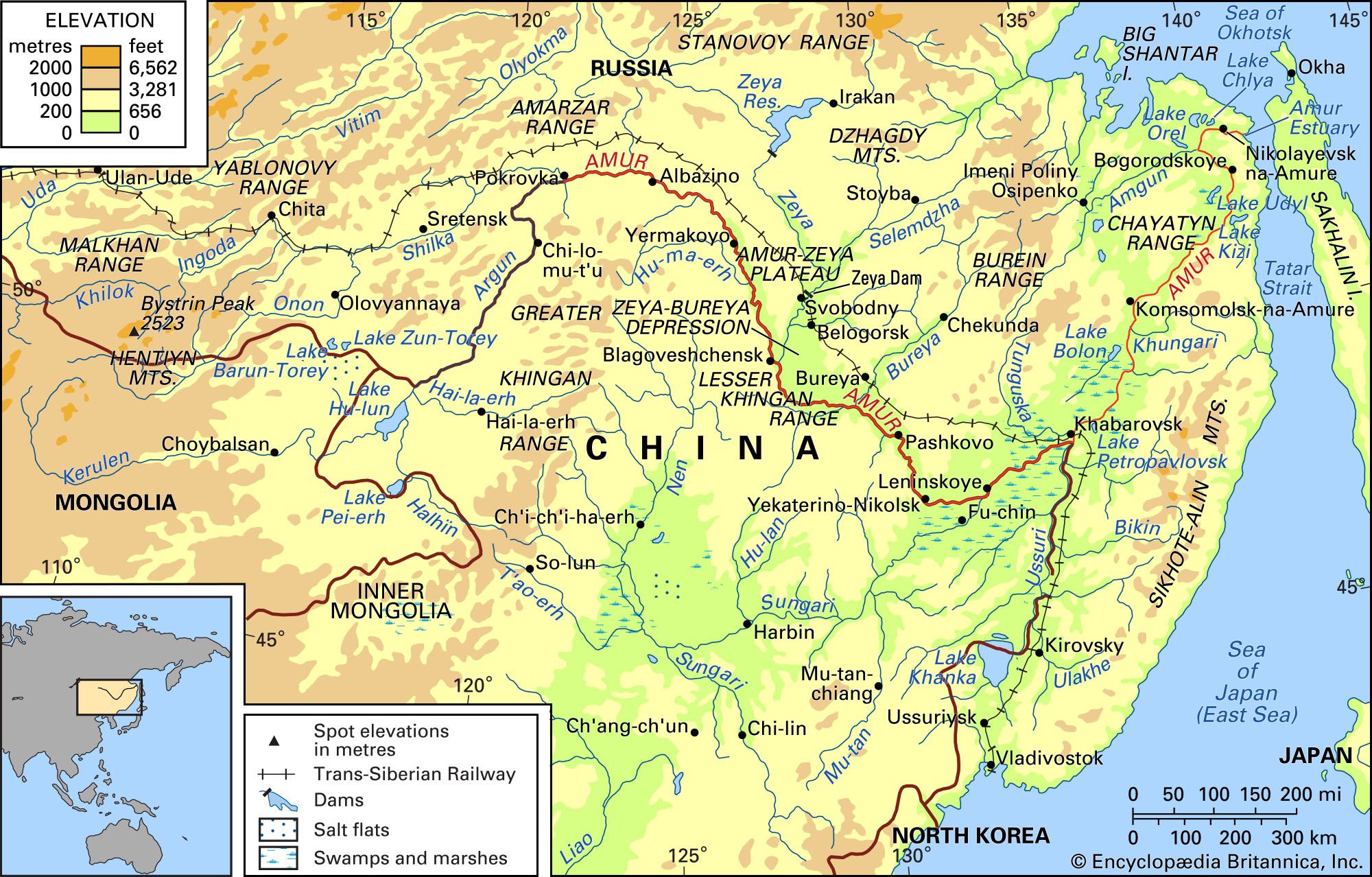
The Acer ginnala is a small to medium-sized tree that typically reaches heights of 15 to 25 feet (4.5 to 7.5 meters). It belongs to the Acer genus, which encompasses a diverse range of maple species renowned for their aesthetic appeal and ecological importance. The Amur River Maple is native to the Amur River region, hence its name, which spans parts of Russia, China, and Korea. This tree has adapted to thrive in a variety of habitats, including forests, riverbanks, and open woodlands.
Distinctive Features
One of the most striking features of the Amur River Maple is its foliage. The leaves are typically 3 to 5 inches (7.5 to 12.5 cm) long, with a distinctively lobed shape. They emerge in spring with a light green hue, gradually transforming into a rich, dark green as the season progresses. In the fall, the leaves put on a spectacular display, turning shades of yellow, orange, and red, adding a vibrant touch to any landscape.
In addition to its foliage, the Amur River Maple boasts delicate, yellowish-green flowers that appear in clusters during late spring. These flowers, while not as showy as some other maple species, are a vital source of nectar for pollinators such as bees and butterflies. The tree also produces small, winged samaras, which contain the seeds and are dispersed by the wind, aiding in the tree's natural propagation.
Cultivation and Care

The Amur River Maple is highly adaptable and can thrive in a range of soil types and conditions. It prefers well-drained soil but can tolerate some drought once established. This maple species is known for its hardiness and can withstand temperatures as low as -40°F (-40°C), making it an excellent choice for regions with harsh winters.
Soil and Sunlight Requirements
While the Amur River Maple can tolerate partial shade, it thrives in full sun to partial shade conditions. When planted in full sun, the tree tends to develop a more compact and dense form, making it an ideal choice for smaller gardens or urban landscapes. As for soil, it prefers slightly acidic to neutral pH levels and can adapt to various soil textures, from sandy to clay-rich soils.
Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning is an essential aspect of maintaining the health and aesthetics of the Amur River Maple. Regular pruning helps to promote a strong branch structure and encourages the growth of vibrant foliage. It is recommended to prune the tree during its dormant season, typically in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. Removing dead or diseased branches and thinning out crowded areas can improve air circulation and reduce the risk of disease.
Landscape Design and Ornamental Value

The Amur River Maple’s versatility and aesthetic appeal make it a popular choice for landscape designers and gardeners. Its compact size makes it well-suited for smaller spaces, such as urban gardens, courtyards, and residential landscapes. When planted in groups or as a specimen tree, it can create a stunning visual impact, particularly during the vibrant fall season.
Ecological Significance
Beyond its ornamental value, the Amur River Maple plays a crucial role in ecosystems. As mentioned earlier, its flowers provide a valuable source of nectar for pollinators, contributing to the overall health and diversity of local ecosystems. Additionally, the tree’s dense foliage offers shelter and nesting sites for birds and small mammals, enhancing biodiversity in the area.
Urban Benefits
In urban settings, the Amur River Maple can help mitigate the urban heat island effect by providing shade and reducing the absorption of solar radiation. Its ability to tolerate pollution and compacted soils makes it an ideal choice for urban landscapes, where it can help improve air quality and create a more pleasant environment for residents.
Performance and Growth Analysis

The Amur River Maple is known for its rapid growth, particularly in its early years. Under optimal conditions, it can grow up to 2 feet (60 cm) per year, allowing it to reach a mature height relatively quickly. This rapid growth, combined with its hardiness and adaptability, makes it a popular choice for those seeking a fast-growing, low-maintenance tree.
| Growth Rate | Up to 2 feet (60 cm) per year |
|---|---|
| Mature Height | 15 to 25 feet (4.5 to 7.5 meters) |
| Soil Preference | Well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral pH |
| Sunlight Requirements | Full sun to partial shade |
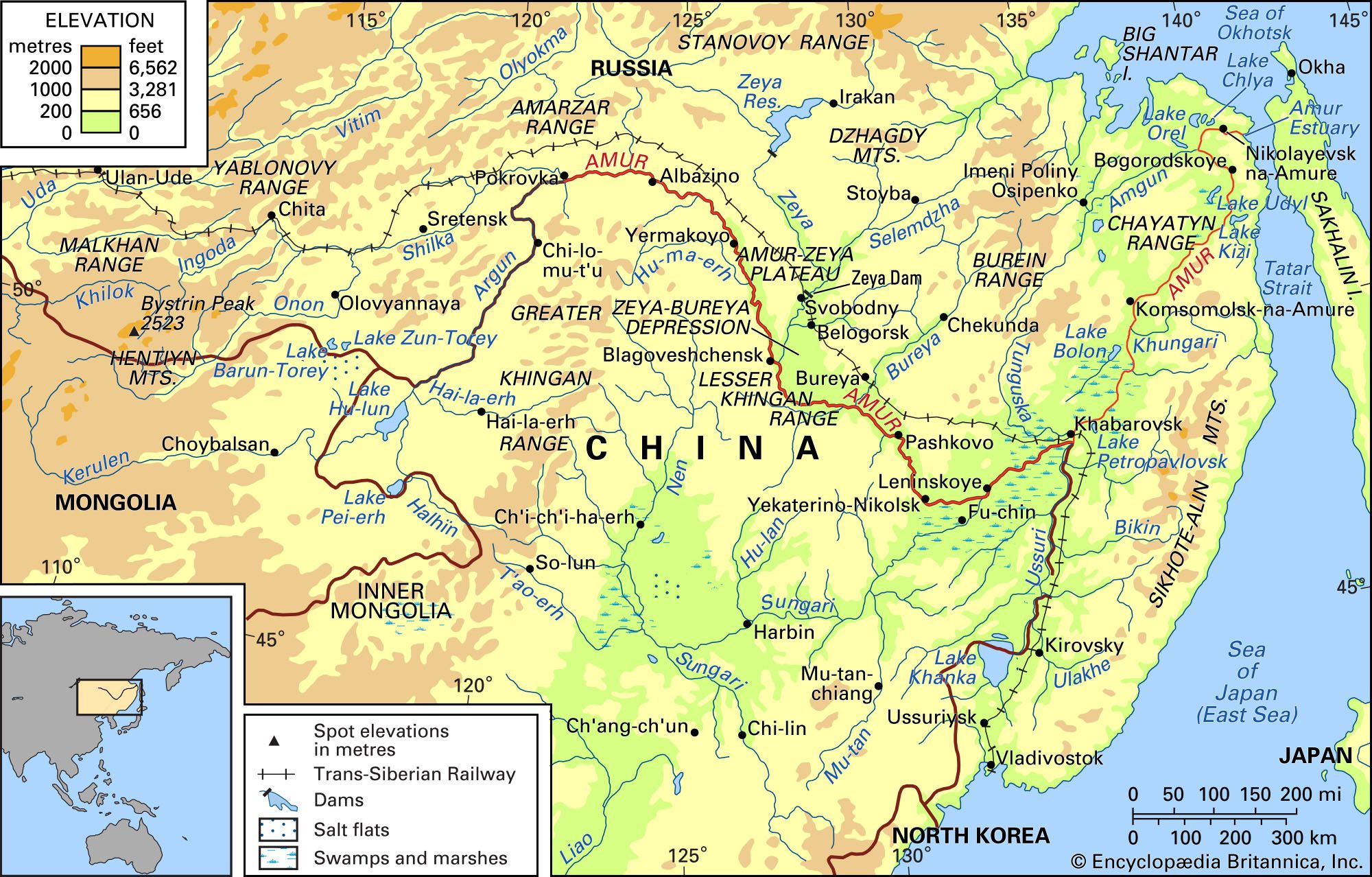
Comparative Analysis
When compared to other maple species, the Amur River Maple stands out for its hardiness and adaptability. While it may not reach the towering heights of some other maple species, such as the Sugar Maple (Acer saccharum), its compact size and rapid growth make it an excellent choice for smaller spaces. Additionally, its vibrant fall foliage and ecological benefits set it apart as a valuable addition to any landscape.
Future Implications and Conservation
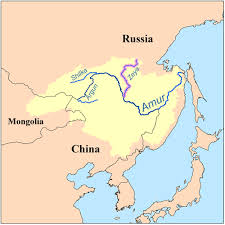
As with many plant species, the Amur River Maple faces potential threats from habitat loss and climate change. While it is not currently considered endangered, conservation efforts are essential to ensure its long-term survival and continued presence in natural ecosystems. One way to contribute to its conservation is by incorporating it into landscaping projects and promoting its cultivation in sustainable, eco-friendly practices.
Conclusion

The Amur River Maple, with its elegant form, vibrant foliage, and ecological significance, is a valuable addition to any landscape. Its adaptability, hardiness, and rapid growth make it an ideal choice for a wide range of settings, from urban gardens to natural woodlands. By understanding its unique characteristics and cultivation requirements, we can ensure its successful growth and contribute to the preservation of this beautiful maple species.
How can I propagate the Amur River Maple?
+The Amur River Maple can be propagated through seeds or cuttings. For seed propagation, collect the samaras in the fall and allow them to dry. Sow the seeds in well-drained soil and keep them moist until germination. For cutting propagation, take semi-hardwood cuttings in late summer and root them in a well-drained medium. Both methods require patience and careful attention to ensure successful propagation.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect the Amur River Maple?
+While the Amur River Maple is generally resistant to many pests and diseases, it can occasionally be affected by aphids, scale insects, and leaf spots. Regular monitoring and proper care can help prevent these issues. If pests or diseases are detected, it is recommended to consult with a local horticulture expert or arborist for appropriate treatment options.
Can the Amur River Maple be grown in containers?
+Yes, the Amur River Maple can be successfully grown in containers. Choose a container with good drainage and use a well-drained potting mix. Regular watering and fertilizing are essential to maintain the tree’s health. However, it is important to note that container-grown trees may have a slower growth rate compared to those planted in the ground.