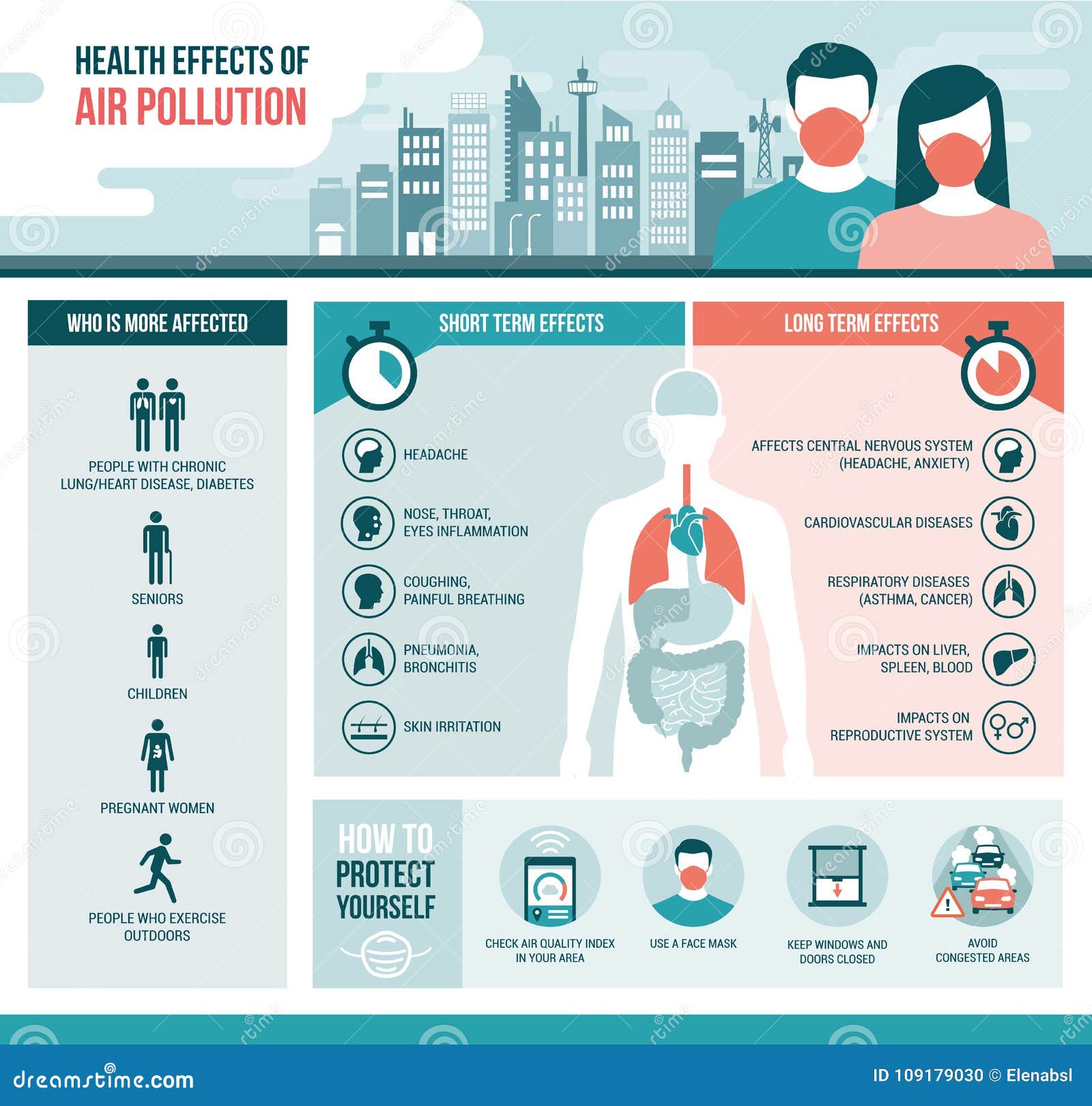
12 Ways Agriculture's Impact On Air Quality Affects Our Health

Agriculture is a vital industry that provides us with food, fuel, and various other resources, but it also has a significant impact on air quality. The practices and processes involved in agriculture can release pollutants into the atmosphere, leading to potential health risks for both humans and the environment. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into 12 key ways in which agriculture's influence on air quality directly affects our health, shedding light on the complex interplay between agricultural practices and public well-being.
1. Particulate Matter Emissions

Agricultural activities, such as tilling, harvesting, and the use of heavy machinery, contribute to the release of particulate matter into the air. These tiny particles, often referred to as PM2.5 or PM10, can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, causing respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and even contributing to the development of chronic diseases.
Health Risks Associated with Particulate Matter
Exposure to high levels of particulate matter has been linked to an increased risk of asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions. Prolonged exposure can lead to the exacerbation of existing respiratory ailments and may even contribute to the onset of cardiovascular diseases. The fine particles can enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to inflammation and oxidative stress.
| Particulate Matter (PM) Size | Health Effects |
|---|---|
| PM2.5 | Respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and potential development of chronic diseases. |
| PM10 | Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, as well as respiratory symptoms. |

2. Ammonia Emissions
Animal agriculture, particularly the intensive rearing of livestock, is a significant source of ammonia emissions. Ammonia, a gas released from animal waste and fertilizer application, can react with other pollutants in the atmosphere to form fine particulate matter and harmful aerosols.
Impact on Air Quality and Health
Ammonia emissions contribute to the formation of secondary particulate matter, which can be inhaled and lead to respiratory problems. Additionally, ammonia can react with sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides to form ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate, respectively. These compounds are known to have adverse effects on respiratory health, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
3. Nitrogen Oxide Emissions

Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a group of gases primarily produced by combustion processes, including those in agricultural machinery and the burning of fossil fuels for agricultural purposes. These gases contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog, and can have detrimental effects on respiratory health.
Ozone and Its Health Implications
Ground-level ozone, when inhaled, can irritate the respiratory tract, leading to coughing, throat irritation, and reduced lung function. Prolonged exposure to ozone is associated with an increased risk of respiratory infections and the exacerbation of conditions like asthma. Additionally, ozone can react with other pollutants to form secondary pollutants, further complicating air quality issues.
4. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Agricultural activities, especially those involving the use of pesticides and fertilizers, release volatile organic compounds into the atmosphere. VOCs can react with nitrogen oxides to form ground-level ozone and contribute to the formation of secondary pollutants.
VOCs and Their Health Effects
VOCs, when inhaled, can cause eye, nose, and throat irritation. Certain VOCs are known to be carcinogenic, and long-term exposure may increase the risk of developing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, VOCs can contribute to the formation of photochemical smog, further degrading air quality.
5. Pesticide Drift

The application of pesticides in agriculture can lead to pesticide drift, where these chemicals are carried by wind and deposited in unintended areas. Pesticide drift can expose individuals, especially those living or working near agricultural fields, to harmful chemicals, potentially leading to acute and chronic health effects.
Health Risks of Pesticide Exposure
Acute exposure to pesticides can result in symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, and skin irritation. Chronic exposure has been linked to neurological disorders, reproductive issues, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Children and pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of pesticide exposure.
6. Dust Storms and Soil Erosion

Intensive agricultural practices, such as excessive tilling and improper land management, can contribute to soil erosion and the formation of dust storms. These dust particles, when inhaled, can have adverse effects on respiratory health.
Impact of Dust Storms
Dust storms can transport fine particulate matter over long distances, exposing a wider population to these harmful particles. The inhalation of dust particles can lead to respiratory issues, including coughing, wheezing, and reduced lung function. Prolonged exposure to dust storms may also increase the risk of developing chronic respiratory diseases.
7. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
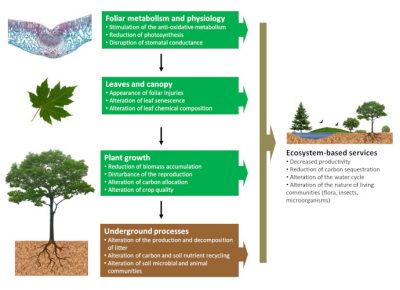
Agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through the production of methane and nitrous oxide. These gases, when released into the atmosphere, contribute to global warming and climate change, which can have far-reaching implications for human health.
Climate Change and Health
Climate change, driven by agricultural emissions, can lead to extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, and floods. These events can directly impact human health, increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses, waterborne diseases, and the spread of vector-borne diseases. Additionally, climate change can disrupt food production and access to clean water, further compromising public health.
8. Air Pollution and Agricultural Workers

Agricultural workers are often exposed to higher levels of air pollutants due to their proximity to agricultural activities. This exposure can lead to a range of health issues, including respiratory problems, skin conditions, and potential long-term health consequences.
Protecting Agricultural Workers
Implementing measures to reduce air pollution in agricultural settings is crucial for the well-being of workers. This includes the use of personal protective equipment, such as respirators, and the adoption of best practices to minimize the release of pollutants. Regular health monitoring and access to medical care can also help mitigate the health risks associated with agricultural work.
9. Impact on Vulnerable Populations

Certain populations, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, are more vulnerable to the health effects of air pollution from agricultural sources. These groups may experience more severe symptoms and have a higher risk of developing chronic diseases.
Protecting Vulnerable Communities
Implementing targeted measures to protect vulnerable populations is essential. This can include the establishment of air quality monitoring systems in areas with high agricultural activity, the development of educational programs to raise awareness about air pollution risks, and the provision of access to healthcare services for those affected by agricultural air pollution.
10. Air Quality and Food Safety

Air pollution from agricultural sources can also impact food safety. Pesticide drift, for example, can contaminate crops, leading to the presence of harmful chemicals in the food supply. Additionally, air pollutants can affect the nutritional quality of crops, potentially impacting human health.
Ensuring Food Safety
Implementing strict regulations and monitoring systems to minimize pesticide drift and other forms of air pollution is crucial for food safety. This includes the use of precision agriculture techniques, such as targeted pesticide application and the adoption of sustainable farming practices, to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture.
11. The Role of Policy and Regulation
Effective policies and regulations play a crucial role in mitigating the health impacts of agriculture on air quality. Governments and regulatory bodies can implement measures to reduce emissions, promote sustainable practices, and protect public health.
Key Policy Interventions
- Emission standards for agricultural machinery and equipment.
- Regulations on the use and application of pesticides and fertilizers.
- Support for the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision farming and organic farming.
- Incentives for farmers to invest in air pollution control technologies.
12. Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the link between agriculture and air quality is essential for fostering a sense of responsibility and promoting sustainable practices. Educating the public about the health risks associated with air pollution from agricultural sources can lead to informed choices and the adoption of measures to protect their well-being.
Empowering Communities
Community engagement and education programs can play a vital role in addressing air quality issues related to agriculture. By providing information about air pollution sources, health risks, and preventive measures, communities can take an active role in advocating for cleaner air and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
What are the key sources of air pollution in agriculture?
+Key sources of air pollution in agriculture include particulate matter emissions from machinery and tilling, ammonia emissions from animal agriculture, nitrogen oxide emissions from combustion processes, volatile organic compounds from pesticide and fertilizer use, and greenhouse gas emissions from livestock and fertilizer application.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can air pollution from agriculture be reduced?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Measures to reduce air pollution from agriculture include implementing precision farming techniques, adopting sustainable practices like organic farming, using air pollution control technologies, and promoting the use of renewable energy sources in agricultural operations.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are the long-term health effects of exposure to agricultural air pollutants?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Long-term exposure to agricultural air pollutants can lead to the development of chronic respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, neurological disorders, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Vulnerable populations, such as children and individuals with pre-existing conditions, are at a higher risk of experiencing these health effects.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



