12 Army Pt Safety Guidelines To Prevent Injury

In military training, physical fitness is an essential aspect of a soldier's readiness and resilience. However, the intense nature of army physical training (PT) sessions can pose a significant risk of injury if not approached with proper guidelines and precautions. Here, we delve into 12 crucial safety guidelines that can help prevent injuries during army PT, ensuring that soldiers remain combat-ready and physically capable.
Warm-up and Cool-down Protocols

Warm-up routines are an integral part of any physical activity, and army PT is no exception. A proper warm-up routine prepares the body for the upcoming physical demands, reducing the risk of muscle strains and pulls. Similarly, a cool-down routine is essential to gradually bring the body back to its resting state, preventing blood pooling and aiding in muscle recovery.
Warm-up Strategies
A well-designed warm-up should include a combination of light aerobic exercises, dynamic stretching, and mobility drills. For instance, a warm-up could begin with a 5-minute jog, followed by dynamic stretches like leg swings, arm circles, and torso rotations. This helps increase heart rate, improve blood flow to the muscles, and prepare the body for more intense physical activity.
| Warm-up Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Light Aerobic Exercise | Low-intensity activities like jogging, cycling, or rowing to increase heart rate and warm up the body. |
| Dynamic Stretching | Active stretches that involve movement, such as leg swings or torso twists, to improve range of motion and prepare muscles for activity. |
| Mobility Drills | Specific exercises to improve joint mobility and prepare the body for the demands of PT, such as shoulder dislocations or hip rotations. |

Cool-down Techniques
A cool-down routine typically involves a combination of static stretching and light aerobic exercise. Static stretching helps to improve flexibility and reduce muscle soreness. For example, a cool-down might include 10-15 minutes of static stretches targeting major muscle groups, followed by a slow, gentle jog to help remove lactic acid from the muscles.
Hydration and Nutrition

Proper hydration and nutrition are fundamental to any athlete’s performance and recovery, and soldiers are no exception. Maintaining adequate fluid and electrolyte balance is crucial to prevent dehydration and heat-related illnesses during intense physical activity.
Hydration Strategies
Soldiers should aim to drink fluids regularly throughout the day, not just during PT sessions. The goal is to stay properly hydrated before, during, and after physical activity. It’s recommended to drink 16-20 ounces of fluid 2-3 hours before exercise, and another 8-10 ounces of fluid every 10-20 minutes during exercise. After PT, soldiers should continue to rehydrate, aiming to drink 24 ounces of fluid for every pound of body weight lost during exercise.
Nutrition for Recovery
Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle recovery and repair. Consuming a balanced diet that includes lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats is essential. Additionally, soldiers should consider incorporating post-workout nutrition, such as protein shakes or bars, to aid in muscle recovery and repair. This can help reduce muscle soreness and speed up the recovery process.
Progressive Training Intensities
One of the key principles of injury prevention in army PT is progressive training intensities. This means gradually increasing the intensity, duration, and complexity of exercises over time. By doing so, soldiers can build up their physical resilience and endurance, reducing the risk of injury.
Progressive Resistance Training
Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, should be progressed gradually. This means starting with lighter weights or lower repetition ranges and gradually increasing the load or difficulty over time. For example, a soldier might start with 3 sets of 10 repetitions of a particular exercise at a manageable weight, and over several weeks, increase the weight or number of repetitions to continue challenging the body.
Gradual Increase in Cardio Intensities
Cardiovascular exercises, such as running or rowing, should also be progressed gradually. Soldiers should start with shorter distances or durations at a comfortable pace, and over time, increase the distance, duration, or intensity of the exercise. This progressive approach allows the body to adapt to the increasing physical demands, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
Proper Technique and Form

Maintaining proper technique and form during exercises is crucial to prevent injuries. Incorrect form can place excessive stress on certain muscle groups or joints, leading to potential injuries. Instructors and fellow soldiers should provide feedback and corrections to ensure proper technique is maintained.
Technique Drills
Incorporating technique drills into army PT sessions can help soldiers master the proper form for various exercises. These drills focus on breaking down the movement into smaller, more manageable parts, allowing soldiers to understand and execute the exercise correctly. For example, a technique drill for a pull-up might involve practicing the proper hand placement, body positioning, and pulling motion without actually lifting the entire body weight.
Video Analysis
Video analysis can be a powerful tool to help soldiers visualize and correct their technique. By recording soldiers during PT sessions and reviewing the footage, instructors can provide detailed feedback on areas where form could be improved. This visual feedback can be highly effective in helping soldiers understand and correct their technique.
Equipment Maintenance and Safety
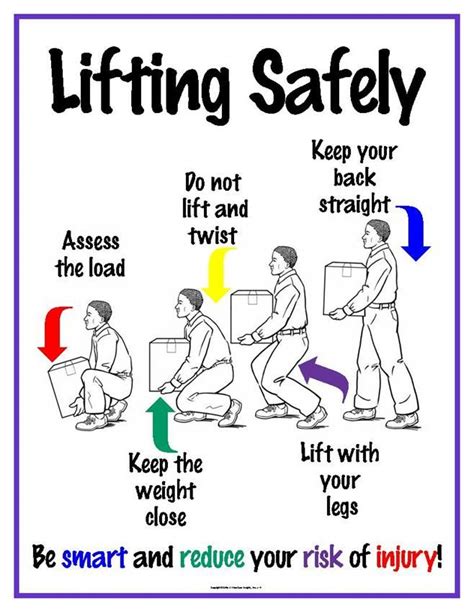
Maintaining and using equipment properly is essential to prevent injuries. This includes regular inspection and maintenance of all equipment used in army PT, from weights and bars to treadmills and rowing machines.
Equipment Inspection
All equipment should be inspected regularly for signs of wear and tear, damage, or malfunction. This includes checking for loose bolts, frayed cables, or other potential hazards. Any equipment found to be unsafe should be immediately removed from use and repaired or replaced.
Safe Equipment Use
Soldiers should be trained on the proper use of all equipment. This includes understanding the correct way to adjust equipment to their body size and how to properly secure themselves during exercises. For example, when using a squat rack, soldiers should know how to properly adjust the safety bars and how to use the rack’s safety features in case of a failed lift.
Rest and Recovery

Rest and recovery are essential components of any training program, including army PT. Adequate rest allows the body to repair and rebuild muscle tissue, helping to prevent overtraining and reduce the risk of injury.
Scheduled Rest Days
Incorporating scheduled rest days into the PT program is crucial. These rest days allow the body to recover and prepare for the next training session. Rest days don’t necessarily mean complete inactivity; they can involve active recovery activities like light walking, swimming, or yoga, which can help improve blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
Sleep and Recovery
Getting adequate sleep is vital for recovery. Soldiers should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. This allows the body to repair and regenerate muscle tissue, helping to prevent fatigue and reduce the risk of injury.
Injury Recognition and Reporting

Recognizing and reporting injuries is crucial to prevent further harm and ensure proper treatment. Soldiers should be educated on the signs and symptoms of various injuries and encouraged to report any pain, discomfort, or injury immediately.
Signs and Symptoms of Injury
Soldiers should be aware of the following signs and symptoms of injury:
- Sharp or persistent pain during or after exercise
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around a joint or muscle
- Loss of strength or range of motion
- Popping or cracking sounds during movement
- Persistent stiffness or soreness
Reporting Procedures
Soldiers should be familiar with the reporting procedures for injuries. This typically involves notifying a supervisor or medical staff as soon as possible. Early reporting allows for prompt medical assessment and treatment, which can help prevent further injury and speed up recovery.
Individualized Training Plans
Every soldier is unique, with different physical capabilities, strengths, and weaknesses. Implementing individualized training plans can help ensure that soldiers are challenged appropriately, reducing the risk of injury.
Assessing Individual Capabilities
Before starting a training program, soldiers should undergo a comprehensive fitness assessment to determine their current physical capabilities. This assessment can help identify areas of strength and weakness, allowing for the development of a tailored training plan.
Customized Training Programs
Based on the fitness assessment, soldiers can be assigned customized training programs. These programs should take into account the soldier’s current fitness level, goals, and any existing injuries or limitations. By tailoring the training to the individual, soldiers can progress at a pace that’s appropriate for them, reducing the risk of overtraining or injury.
Environmental Considerations

Environmental factors, such as weather conditions and terrain, can significantly impact the risk of injury during army PT. Instructors should be mindful of these factors and adjust training programs or equipment use accordingly.
Weather Conditions
Extreme weather conditions, such as high heat or cold, can increase the risk of injury. In hot weather, soldiers are at risk of heat-related illnesses, while in cold weather, they may be more prone to muscle strains or pulls. Instructors should monitor weather conditions and adjust training intensity or duration as needed. Additionally, soldiers should be educated on the signs and symptoms of heat-related illnesses and how to prevent them.
Terrain and Surface Considerations
The terrain and surface on which soldiers train can also impact the risk of injury. For example, running on hard surfaces like concrete can increase the risk of joint injuries, while running on soft surfaces like grass or sand can provide more cushioning. Instructors should consider the terrain and surface when planning PT sessions, and soldiers should be aware of the potential risks associated with different surfaces.
Progressive Flexibility Training

Flexibility training is an important component of army PT, as it can help improve range of motion and reduce the risk of injury. However, flexibility training should be progressed gradually to avoid overstretching or tearing muscles.
Dynamic and Static Stretching
Dynamic stretching, as mentioned earlier, is an important part of the warm-up routine. Static stretching, on the other hand, is typically done during the cool-down. Static stretches should be held for 15-30 seconds and repeated 2-4 times. It’s important to avoid bouncing or jerking during static stretches, as this can lead to muscle tears.
Progressive Flexibility Goals
Soldiers should set progressive flexibility goals, aiming to gradually increase their range of motion over time. This can be done by tracking their flexibility progress over several weeks or months. For example, a soldier might start with a goal of touching their toes during a seated forward fold, and over time, work towards being able to place their palms flat on the ground.
Core Strengthening Exercises
Core strengthening exercises are vital to improving overall stability and balance, which can help prevent injuries during physical activity. The core muscles include the abdominals, back muscles, and hip muscles.
Core Exercise Examples
There are numerous core exercises that soldiers can incorporate into their PT routine. Some examples include:
- Planks: Holding a push-up position while resting on the forearms instead of the hands.
- Russian Twists: Sitting on the floor with knees bent and feet flat on the ground, twist the torso from side to side while holding a weight or medicine ball.
- Mountain Climbers: Starting in a high plank position, bring one knee towards the chest, then switch legs rapidly, mimicking the motion of running.
- Leg Raises: Hanging from a pull-up bar, lift the legs towards the chest, then lower them back down in a controlled manner.
Incorporating Core Exercises
Core exercises can be incorporated into army PT sessions in various ways. For example, soldiers might perform a set of core exercises as part of their warm-up routine, or they might be included as a circuit between other exercises during the main workout.
Instructor Education and Training
Instructors play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of soldiers during army PT. They should be well-educated and trained in proper exercise techniques, injury prevention, and emergency response.
Instructor Qualifications
Instructors should have a strong background in fitness and exercise science, and ideally, they should be certified through a reputable fitness organization. Additionally, they should have specific training in military-style physical training and be familiar with the unique demands and challenges faced by soldiers.
Ongoing Education
Instructors should participate in ongoing education and training to stay up-to-date with the latest research and best practices in fitness and injury prevention. This can include attending conferences, workshops, or online courses, as well as regularly reviewing scientific literature on exercise science and sports medicine.
Mental Resilience and Focus
Mental resilience and focus are key components of injury prevention in army PT. Soldiers who are mentally sharp and focused are better able to recognize and respond to potential hazards, reducing the risk of injury.
Mindfulness and Awareness
Instructors can incorporate mindfulness practices into army PT sessions to help soldiers stay focused and aware during exercises. This can include simple breathing exercises, body scans, or short meditation breaks. By improving their mindfulness, soldiers can enhance their focus and awareness, reducing the risk of injury due to distraction or lack of attention.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension, increased risk of injury, and reduced recovery. Instructors should incorporate stress management techniques into army PT sessions, such as progressive muscle relaxation, visualization, or guided imagery. These techniques can help soldiers reduce stress and tension, improving their overall physical and mental well-being.
What are some common injuries that occur during army PT, and how can they be prevented?
+Common injuries during army PT include muscle strains, joint sprains, and stress fractures. These can often be prevented by following proper warm-up and cool-down protocols, maintaining good technique and form, and progressing training intensities gradually. Additionally, proper hydration, nutrition, and rest are crucial for injury prevention.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How often should soldiers undergo fitness assessments, and what are the benefits of individualized training plans?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Soldiers should undergo fitness assessments at least once a year, or more frequently if there are significant changes in their physical capabilities or training goals. Individualized training plans are beneficial because they take into account a soldier's unique strengths and weaknesses, allowing for a more tailored and effective training program. This can help prevent overtraining and reduce the risk of injury.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some signs of overtraining, and how can soldiers prevent it?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Signs of overtraining include persistent fatigue, decreased performance, increased frequency of injuries, and mood disturbances. To prevent overtraining, soldiers should maintain a balanced training program that includes rest days, progressive intensities, and adequate recovery. It's also important to listen to the body and adjust training plans as needed.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>


